
The space mobility company Bellatrix Aerospace based in Bengaluru formed a formal agreement with Astroscale Japan to improve space sustainability. Through their established cooperation both organizations will work together for improving active debris clearance technologies and satellite care platforms and orbit protection strategies in the long term.
Bellatrix Aerospace signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Astroscale Japan to conduct projects related to active debris removal and satellite servicing as well as sustainable in-orbit mobility. The collaboration between the two parties has space sustainability as its main objective while working to create a better orbital environment.
Key Highlights:
-
Under the terms of this partnership the organizations work together to achieve essential goals that include active debris removal as well as satellite servicing and sustainable in-orbit mobility solutions.
-
The innovative propulsion technologies or space mobility solutions delivered by Bellatrix Aerospace serve as the key strength of this emerging Indian space company.
-
Astroscale Japan leads the field of space debris mitigation while offering its customers measurable services such as satellite life extension support and in-orbit situational monitoring alongside end-of-mission services for disposal.
-
Astroscale proves its technological abilities by operating the ELSA-d and ADRAS-J missions in partnership with JAXA, ESA, U.S. Space Force, UK Space Agency and Eutelsat OneWeb.
-
Bellatrix Aerospace accomplished three successful space flights within one year which resulted in Green Propulsion and Hall-Effect Thruster technology accomplishment
-
Collaboration provides Bellatrix Aerospace with the opportunity to extend into the Japanese space industry market.
What is Space Debris?
Space debris consists of all discarded human-made space items which remain without functionality or serviceability such as broken satellites along with discarded rocket components and remnants from previous collisions alongside detached paint particles. Human space exploration missions have created a priority crisis regarding the accumulation of space debris.
These objects remain in various orbits around Earth and pose potential threats to operational satellites and space missions.
-
Rocket-launching material along with decommissioned satellites represent the main components of space debris.
-
Space debris accumulates primarily in the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) section which ranges between Earth surface and 2,000 km elevation but also remains present in Geostationary Orbit (35,786 km above the Equator).
Current Status of Space Debris
-
A total of 30,000 tracked space debris items exist in satellite orbit around Earth.
-
More than 200,000 space objects measure between 1 to 10 cm and numerous millions consist of smaller materials that are smaller than 1 cm.
-
The total number of debris objects exceeds 34,000 pieces that exceed 10 cm dimensions.
-
The space satellite population now totals 6,718 units and has experienced an additional 2,000 spacecraft since the beginning of 2022.
Causes of Space Debris
-
rising satellite launch: The space debris problem worsened because of rising satellite launch frequency.
-
Many of the orbiting satellites within the half-million spacecraft population belong to SpaceX's Starlink internet service.
-
-
decommissioned satellites: Thousands of decommissioned satellites continue to orbit space because they have been abandoned.
-
anti-satellite tests:The deliberate production of debris through anti-satellite tests has occurred in various countries including China, India and the United States.
-
The 2007 Chinese FengYun-1C test resulted in 25% additional space debris that became trackable.
-
Expanding space industry: The rise of public and private sector investments in space.
-
Fragmentation of space debris: Caused by collision, explosion, and degradation of defunct satellites.
Threats and Challenges Posed by Space Debris
-
Satellite Endangerment: Operational satellites become damaged when they collide with space debris that is floating in orbit.
-
The Russian Cosmos-1275 satellite became destroyed after suffering an impact with space debris during 1981.
-
-
Kessler Syndrome: The unpredictable sequence of destructive orbital collisions could make all orbital traffic completely unusable through Kessler Syndrome.
-
Limiting Future Space Activities: Orbital slots for new missions will probably decrease because growing space debris continues to accumulate.
-
Threat to Space Stations: Space debris has caused ISS operators to adjust their trajectory path 32 times since 1999.
-
Space Pollution: results in difficulty with space operations while causing serious environmental problems.
-
Geopolitical Tensions: Disagreements over liability and responsibility for space debris.
-
The U.S. government reported Russia to the ISS operations team because of the satellite testing event.
-
Space Debris Removal Efforts
International Initiatives:
-
Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC): Established in 1993, with ISRO as a member.
-
COPUOS stands for the Committee on Peaceful Uses of Outer Space which exists as a United Nations body that manages space exploration activities.
-
Clean Space Initiative: A European Space Agency (ESA) program for space sustainability.
-
The European Space Agency has scheduled Clearspace-1 as its inaugural aircraft (2026) that will actively extract space debris from orbital space.
-
The RemoveDEBRIS project was formed to advance debris removal hardware demonstrations.
Indian Initiatives:
-
ISRO System for Safe & Sustainable Operations Management (IS4OM) started operations in 2022 as a system to detect space collision threats.
-
Project Netra functions as an advanced system to detect space debris.
-
During 2022 ISRO executed 21 flight maneuvers to prevent collisions between space objects.
-
ISRO SSA Control Centre: Established in 2020 for monitoring space situational awareness.
Measures Needed to Tackle Space Debris
-
The effort to enhance awareness requires improved tracking models and observation technologies.
-
The establishment of automated systems together with space-navigation protocols will improve inter-agency coordination.
-
New debris production should be addressed by switching to reusable launch vehicles rather than single-use rockets.
-
Research-based development of debris removal technologies should focus on implementing harpoons and magnets along with lasers and slingshots for debris capture.
-
On April 15th 2023 ISRO conducted a successful deorbit procedure for Megha Tropiques-1 following completion of its mission.
-
The organization follows all worldwide protocols for space debris mitigation.
Conclusion
The sustainable operations of space depend heavily on the management of space debris. The alliance between Bellatrix Aerospace and Astroscale Japan creates a fundamental solution for active debris removal and sustainable space mobility to address the space debris issue. Future safe and sustainable space conditions will only be possible through global partnership combined with advancing technologies under rigorous regulations.


 Potential Biosignatures Discovered on Exoplanet K2-18b by JWST
Potential Biosignatures Discovered on Exoplanet K2-18b by JWST India Launches First Native Seed Germination Database for Ecological Restoration
India Launches First Native Seed Germination Database for Ecological Restoration India’s Evolving Approach to Artificial Intelligence Governance and Regulation
India’s Evolving Approach to Artificial Intelligence Governance and Regulation Golden Jubilee of Aryabhata 2025: Celebrating India’s First Satellite and ISRO’s Historic Milestone
Golden Jubilee of Aryabhata 2025: Celebrating India’s First Satellite and ISRO’s Historic Milestone ESA's Biomass Mission 2025: Tracking Global Forest Carbon Storage via Satellite
ESA's Biomass Mission 2025: Tracking Global Forest Carbon Storage via Satellite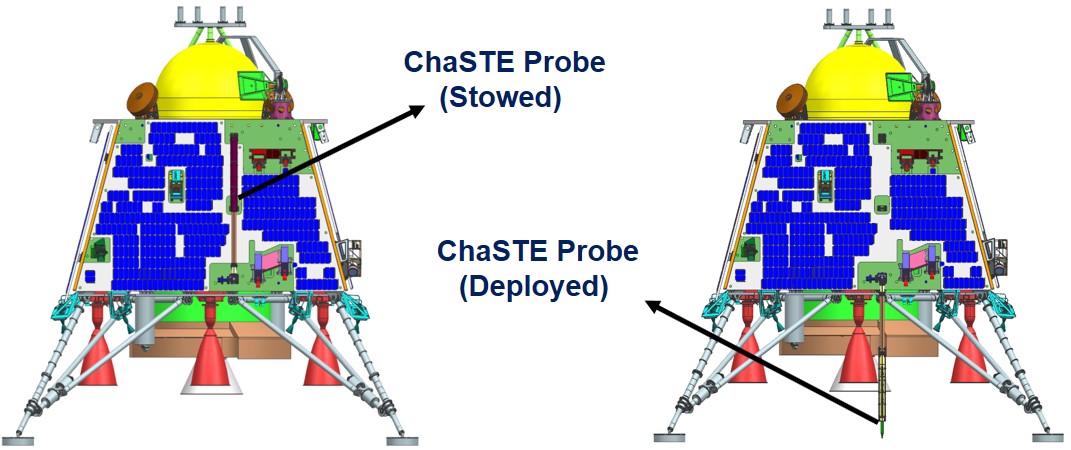 ChaSTE: First In-Situ Measurement of Surface Temperature
ChaSTE: First In-Situ Measurement of Surface Temperature Digital Child Abuse and the Dangers of AI-Based Exploitation
Digital Child Abuse and the Dangers of AI-Based Exploitation SpaceX Successfully Launches Fram2 Mission: First Human Spaceflight Over Earth’s Poles
SpaceX Successfully Launches Fram2 Mission: First Human Spaceflight Over Earth’s Poles Gaia Space Observatory: Achievements and Shutdown
Gaia Space Observatory: Achievements and Shutdown ChatGPT’s viral Studio Ghibli-style images highlight AI copyright concerns
ChatGPT’s viral Studio Ghibli-style images highlight AI copyright concerns






