
A recent landmark defense tech event came to India as it test-fired its first locally developed micro-missile system called the Bhargavastra to counter the growing menace of swarm drones. The trials were carried out at Gopalpur Seaward Firing Ranges on January 12 & 13, 2025 and these are a major leap for India in its military strength. The Bhargavastra system is designed to counter drone threats proactively, provides multiple layers of defense mechanisms, and can be moved around and integrated with the existing defense systems. The ongoing advancement of drone warfare makes Bhargavastra gear up to be very relevant in the battle to protect India’s skies and enhance the country’s defense structure.
Key Features of Bhargavastra:
-
Detection and Engagement:
-
Bhargavastra can identify relatively small-sized incoming drones at a range exceeding 6 kilometers.
-
These threats can be eliminated by the system’s capability of using guided micro-munitions that target the enemy up to distances of 2.5 kilometers away.
-
-
Multi-Layered Defence:
-
It is specifically conceived to be effective when defending against several drone threats at once.
-
It can fire over 64 micro-missiles simultaneously, thus making the system capable of handling mass drone attacks or swarming.
-
-
Mobility and Versatility:
-
Thus, Bhargavastra is mounted on mobile companies that can afford to quickly move to different textures of the territory, including mountainous ones.
-
This flexibility makes it possible for the system to be easily adjusted to the operation’s requirement, making it an awful tool for the Indian Armed Forces.
-
-
Integration with Existing Systems:
-
The system has enhanced Command-and-Control functions to allow compatibility with foremost military networks.
-
Successful Missile Programs of India
-
Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP).
-
Start Date: 1983
-
Completion: 2008
-
Objectives:
-
Build basic Indigenous missile development capability
-
Indigenously develop a spectrum of missiles that can effectively provide coverage to India’s defense forces
-
-
Key Products:
-
Prithvi (Surface-to-Surface Missile)
-
Akash (Surface-to-Air Missile)
-
Nag (Anti-Tank Guided Missile)
-
Trishul (Short-range Surface-to-Air Missile)
-
Agni series (Ballistic Missiles)
-
-
-
India and Russia’s BrahMos Aerospace Joint Venture
-
Established: 1998
-
Partners: India’s Defense Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) & Russia’s NPO Machine building
-
Key Product:
-
BrahMos or supersonic cruise missile
-
BrahMos is among the fastest cruise missiles globally and can be vertically launched from multiple systems.
-
-
-
India’s Ballistic Missile Defence Programme
-
Start Date: 1999
-
Features:
-
End atmosphere and exo-atmosphere intercepting capabilities based on a two-tiered method.
-
Key Products:
-
Prithvi Air Defence (PAD) / Pradyumna (Ballistic Missile Interceptor)
-
Surface to Surface Missile System (SSM) / Prithvi, Agni, Akash, and Trishul / Indigenously developed Ballistic Missile Defence System; Advanced Air Defence (AAD) / Ashwin
-
They enable India to intercept adversaries’ ballistic missile threats and therefore make them stop their attacks.
-
-
-
Independent Projects
-
Since 2008: In fact, after the IGMDP programme India has started several independent missile programmes.
-
Key products:
-
Agni Series (Advanced Ballistic Missiles)
-
K-Missiles (Cruise Missiles)
-
Hypersonic Technology Demonstrator Vehicle (Ongoing development of hypersonic missile technology)
-
-
Types of Missiles
Classification of Missiles based on speed
-
Subsonic Missiles
-
Speed: Below the speed of sound also known as, Mach 1.
-
Examples:
-
U.S. Harpoon (Anti-ship missile)
-
Indian PRITHVI (Short-Range Ballistic Missile)
-
-
-
Supersonic Missiles
-
Speed: Faster than Mach 1 but slower than Mach 5
-
Examples:
-
Russian Iskander (Tactical ballistic missile)
-
Indian BrahMos which is a supersonic cruise missile.
-
-
-
Hypersonic Missiles
-
Speed: At least five times the speed of sound that is over Mach 5.
-
Examples:
-
China DF-ZF (Hypersonic glide vehicle)
-
Russia Avangard
-
India’s Shaurya/ Sagarika (maximum speed 7.5 Mach)
-
-
Classification of Missiles based on Trajectory
-
Ballistic Missiles
-
Trajectory: Ballistic flight with lofted trajectory and glider phase of unpowered free fall following the boost phase
-
Examples:
-
Agni series
-
Prithvi series of Ballistic missiles.
-
-
-
Hypersonic Missiles
-
Feature: Ballistic missile reaching or exceeding hypersonic velocities while re-entering the Earth’s atmosphere
-
Examples:
-
Technology China DF-17 (Hypersonic glide vehicle)
-
Russia Avangard (Boost-glide system).
-
India's Status: The “Technology Demonstration” stage of HGVs
-
-
-
Cruise Missiles
-
Feature: Surface-to-surface missiles seeking targets on land or sea and flying in the Earth’s atmosphere at constant velocities.
-
Types of Cruise Missiles:
-
Subsonic Cruise Missiles
-
Speed is below the speed of sound i.e less than Mach 1
-
Examples:
-
U.S. Tomahawk (BGM-109)
-
-
-
India Subsonic Cruise Indian Nirbhay
-
Intermediate-Range Cruise Missiles (Speed greater than Mach 1 but less than Mach 5)
-
Examples:
-
Bramos (a Supersonic cruise missile that has a speed of Mach 3).
-
-
-
Hypersonic Cruise Missiles (Speed greater than Mach 5).
-
Examples:
-
Russia 3M22 Zircon Hypersonic cruise missile (High speed- Mach 8)
-
India BrahMos II (Under development planned for the speed above Mach 8 based on Zircon)
-
-
-
-
Classification of Missiles based on Propulsion
-
Solid Propulsion
-
Description: Uses high-density fuel such as Hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene (HTPB) fuel. It is affordable, easy to handle, and effective.
-
Examples:
-
Prithvi (Ballistic missile)
-
BrahMos (Cruise missile)
-
-
-
Liquid Propulsion
-
Description: Uses liquid fuels (e.g., Hydrazine, Liquid Hydrogen) and oxidizers (e.g., Nitrogen Tetroxide, Liquid Oxygen). It also offers optimal efficiency and throttle ability as compared to the traditional study.
-
Examples:
-
Agni series ballistic missile system.
-
Akash surface-to-air missile system
-
Note: Agni-Prime was recently successfully tested with solid propellant making the missile lighter than all other Agni series missiles.
-
-
-
Hybrid Propulsion
-
Description: A dual type of propellant, both solid and liquid type.
-
Examples:
-
Used in the prototype of the BrahMos hypersonic cruise missile.
-
-
-
Cryogenic Propulsion
-
Description: It uses liquid oxygen and hydrogen and has a very high energy density.
-
Examples:
-
Used in the Agni-V, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM).
-
-
-
Ramjet/Scramjet Propulsion
-
Description: Air-breathing engines that are utilized for hypersonic ballistic and cruise missile systems.
-
Examples:
-
Under development: India’s HGV (Hypersonic Glide Vehicle)
-
BrahMos II (Cruise Missile missile type hypersonic)
-
-
Conclusion
The successful demonstration of Bhargavastra establishes India as having the potential in the realm of defense technology and demonstrates its ability to contain the new and dangerous threat of swarm drones. As an electronic warfare weapon, Bhargavastra gives a fitting response to any attempt to tamper with Indian airspace and empowers Trident to add more teeth to the Indian Armed Forces.



 IIA Achieves Breakthrough in Measuring Helium Abundance in the Sun
IIA Achieves Breakthrough in Measuring Helium Abundance in the Sun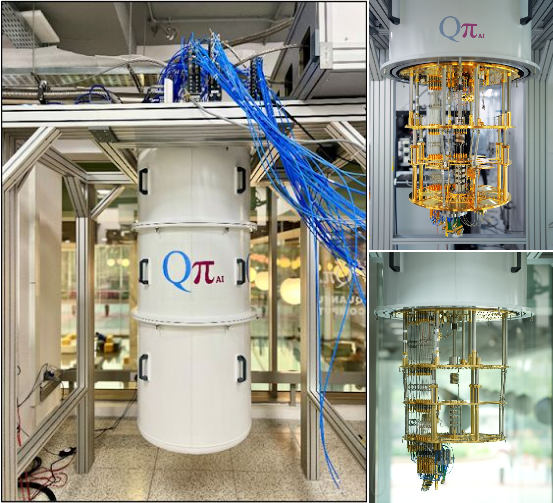 QpiAI Launches India’s First Full-Stack Quantum Computer, QpiAI-Indus, on World Quantum Day
QpiAI Launches India’s First Full-Stack Quantum Computer, QpiAI-Indus, on World Quantum Day ISRO to Send Tardigrades on Axiom-4 Mission: A Step Towards Advancing Space Research
ISRO to Send Tardigrades on Axiom-4 Mission: A Step Towards Advancing Space Research TERI's Nano Sulphur Breakthrough in Mustard Cultivation
TERI's Nano Sulphur Breakthrough in Mustard Cultivation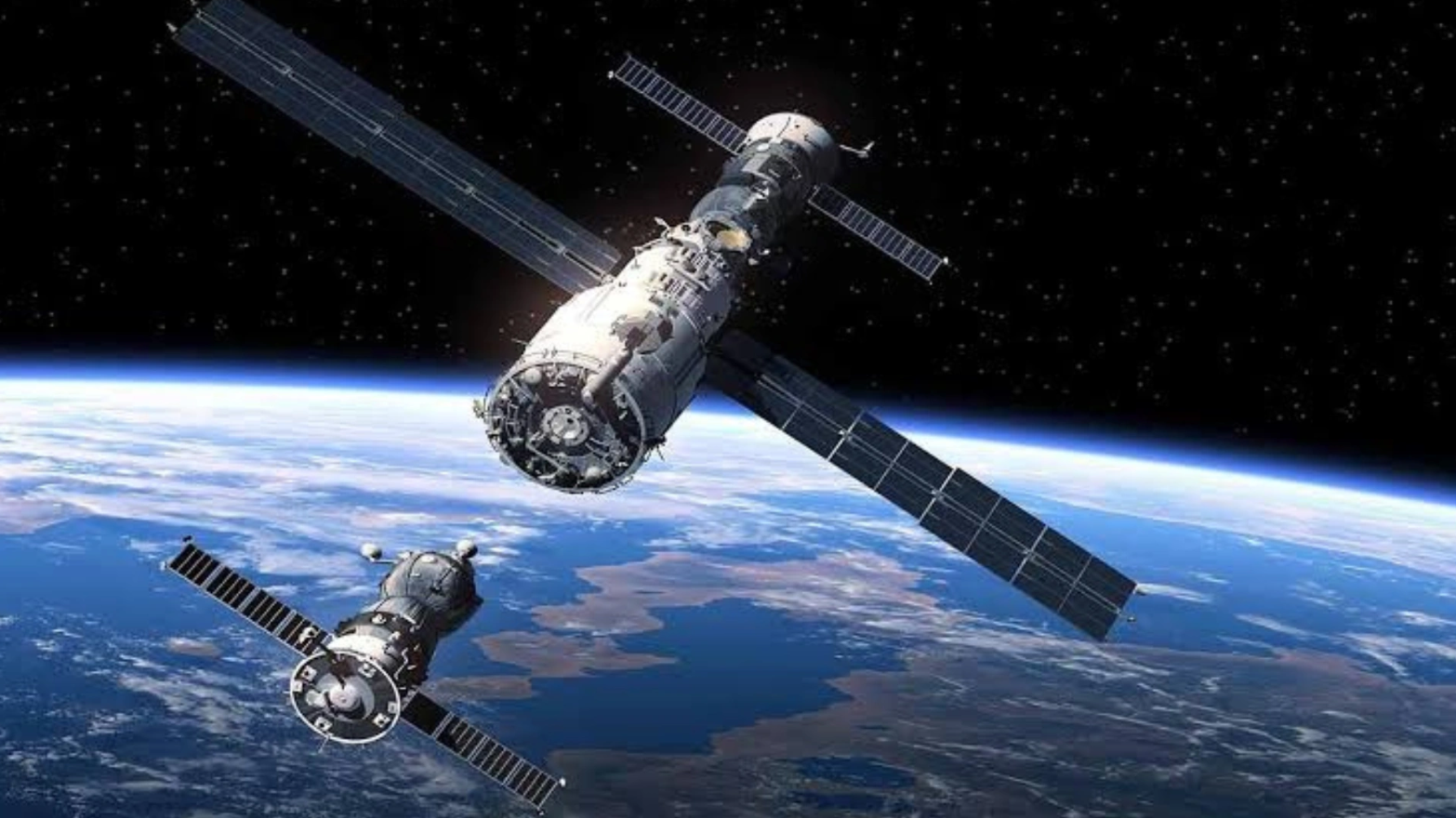 ISRO's Successful Second Docking of Satellites – A Milestone in Space Technology
ISRO's Successful Second Docking of Satellites – A Milestone in Space Technology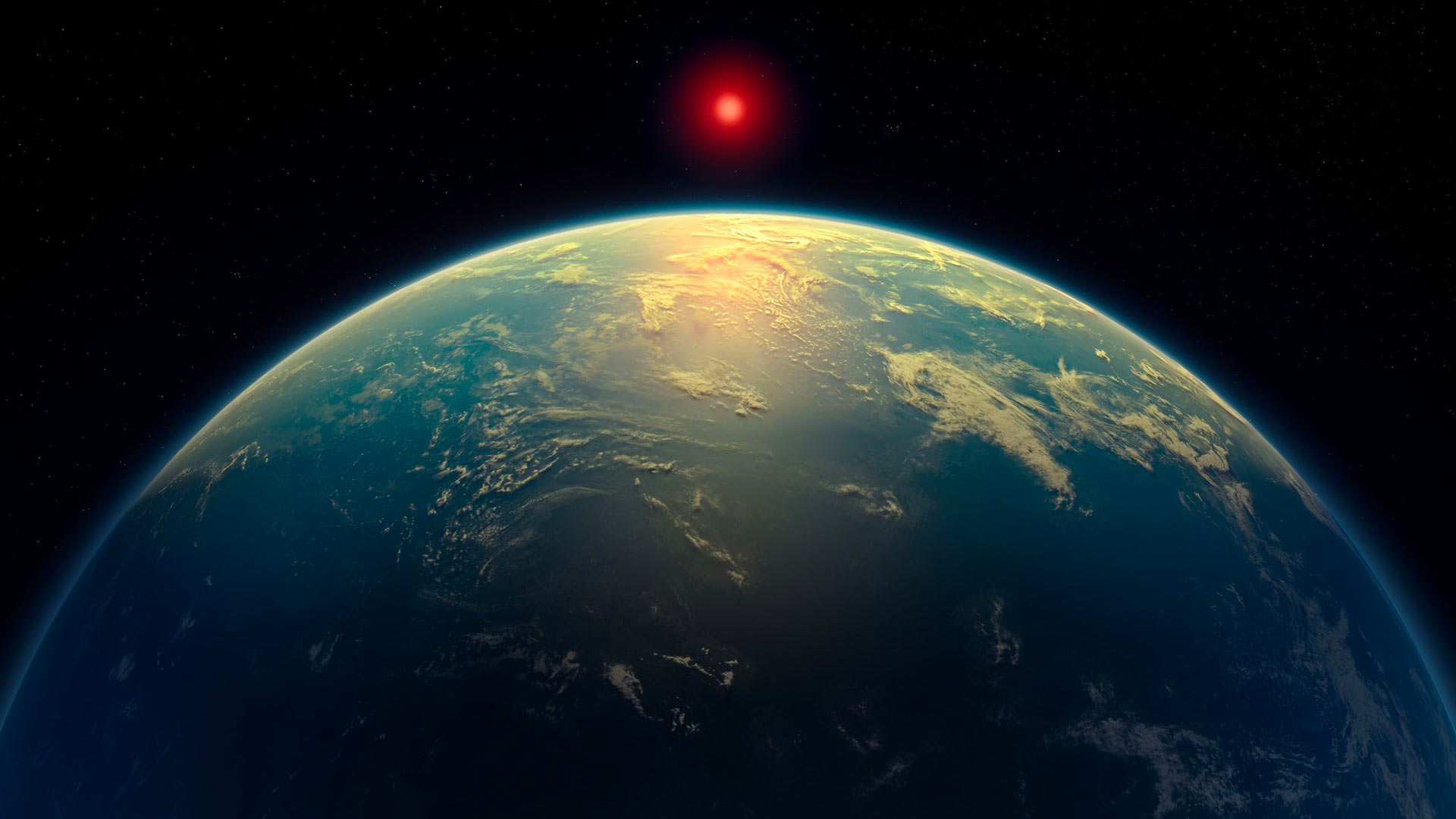 Potential Biosignatures Discovered on Exoplanet K2-18b by JWST
Potential Biosignatures Discovered on Exoplanet K2-18b by JWST India Launches First Native Seed Germination Database for Ecological Restoration
India Launches First Native Seed Germination Database for Ecological Restoration India’s Evolving Approach to Artificial Intelligence Governance and Regulation
India’s Evolving Approach to Artificial Intelligence Governance and Regulation Golden Jubilee of Aryabhata 2025: Celebrating India’s First Satellite and ISRO’s Historic Milestone
Golden Jubilee of Aryabhata 2025: Celebrating India’s First Satellite and ISRO’s Historic Milestone ESA's Biomass Mission 2025: Tracking Global Forest Carbon Storage via Satellite
ESA's Biomass Mission 2025: Tracking Global Forest Carbon Storage via Satellite






