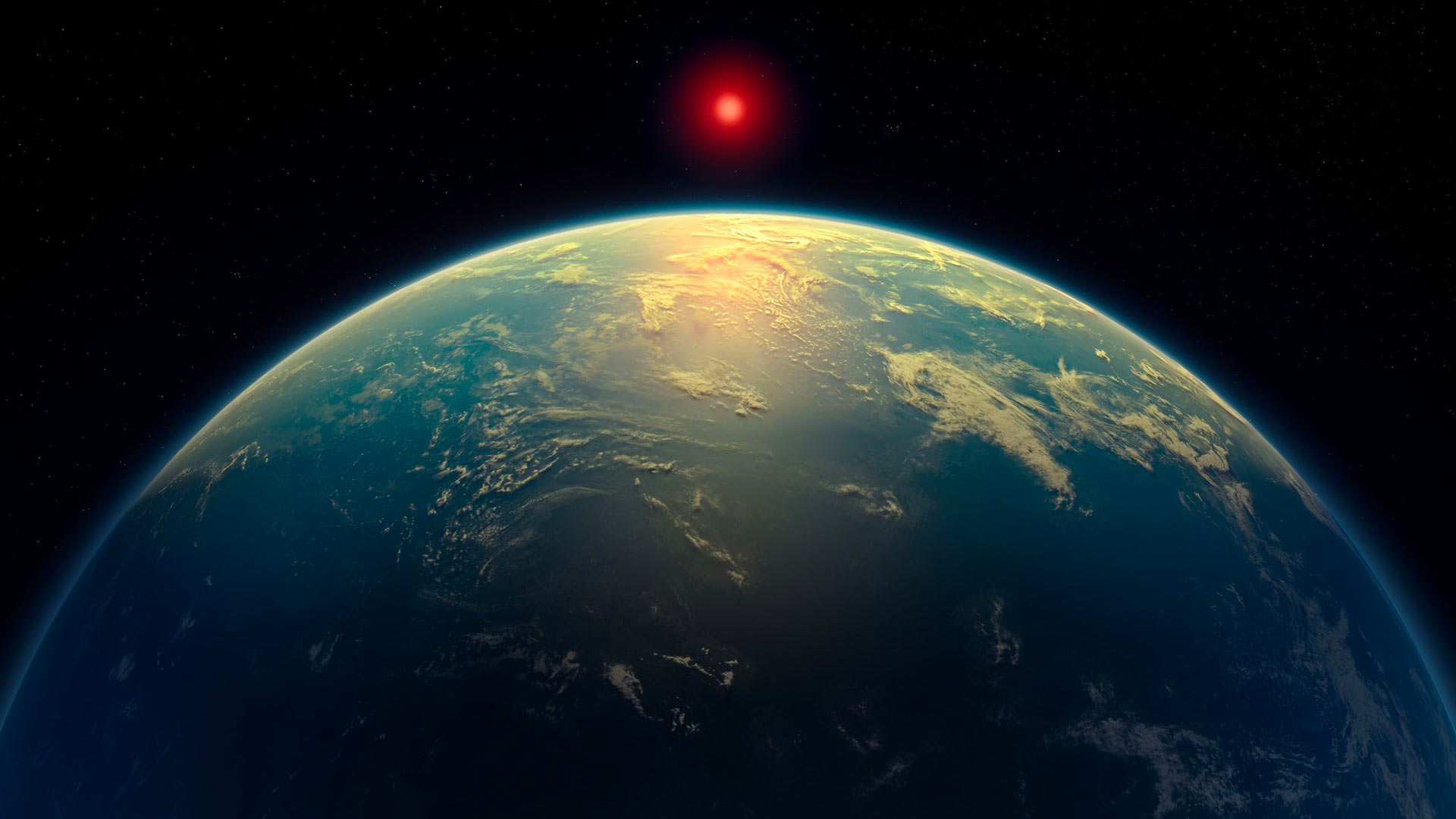

The team of astronomers identified a noteworthy possible biosignature on K2-18b which exists at 124 light-years away from Earth. Scientists at the team utilized the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) to spot atmospheric chemical indicators like Dimethyl Sulfide (DMS) and Dimethyl Disulfide (DMDS) on K2-18b. The substances exist in Earth microbial life publications and marine phytoplankton specifically produce these compounds. Scientists detect promising signs of life on K2-18b through their observations yet conclusive evidence remains under investigation by researchers.
Context:
-
Astronomers have discovered possible hints of potential life beyond our solar system on K2-18b which exists 124 light years away from the earth.
About K2-18b:
Introduction
-
Human exploration of K2-18b remains impossible due to its 124 light-year distance and its two-and-a-half Earth-size dimensions.
-
The small red star orbited by K2-18b exists in the habitable zone which allows liquid water to exist on its surface.
James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) Capabilities:
-
Through its strong capabilities the JWST examines exoplanet atmospheres by making observations of stellar light that passes through the planet's orbit.
-
The observation revealed possible traces of dimethyl sulfide (DMS) and dimethyl disulfide (DMDS) which exist on Earth due to biological processes. Marine phytoplankton together with bacteria produce these chemical substances.
Potential Significance of DMS and DMDS:
-
Scientists confirm that DMS and DMDS remain strictly microbial products which occur only within ocean environments on Earth.
-
Atmospheric observations of these molecules point in the direction of possible biological processes as well as microbial life existing on K2-18b.
-
The molecules exist in two forms and these compounds might form naturally without biological processes which creates uncertainty about the evidence.
Further Research:
-
Researchers ask for additional observations together with data confirmation to draw firm conclusions about the matter.
-
Future research teams will determine whether DMS and other selected chemical markers exist or not.
Conclusion:
Scientists have accomplished a landmark discovery through detecting plausible biosignatures on the exoplanet K2-18b. The recent discovery creates new potential for scientists to evaluate the capabilities of planets existing outside our solar system. Through its new measurements the James Webb Space Telescope functions as an essential tool to study these mysteries as it introduces a new era of astrobiology and space science.


 India Launches First Native Seed Germination Database for Ecological Restoration
India Launches First Native Seed Germination Database for Ecological Restoration India’s Evolving Approach to Artificial Intelligence Governance and Regulation
India’s Evolving Approach to Artificial Intelligence Governance and Regulation Golden Jubilee of Aryabhata 2025: Celebrating India’s First Satellite and ISRO’s Historic Milestone
Golden Jubilee of Aryabhata 2025: Celebrating India’s First Satellite and ISRO’s Historic Milestone ESA's Biomass Mission 2025: Tracking Global Forest Carbon Storage via Satellite
ESA's Biomass Mission 2025: Tracking Global Forest Carbon Storage via Satellite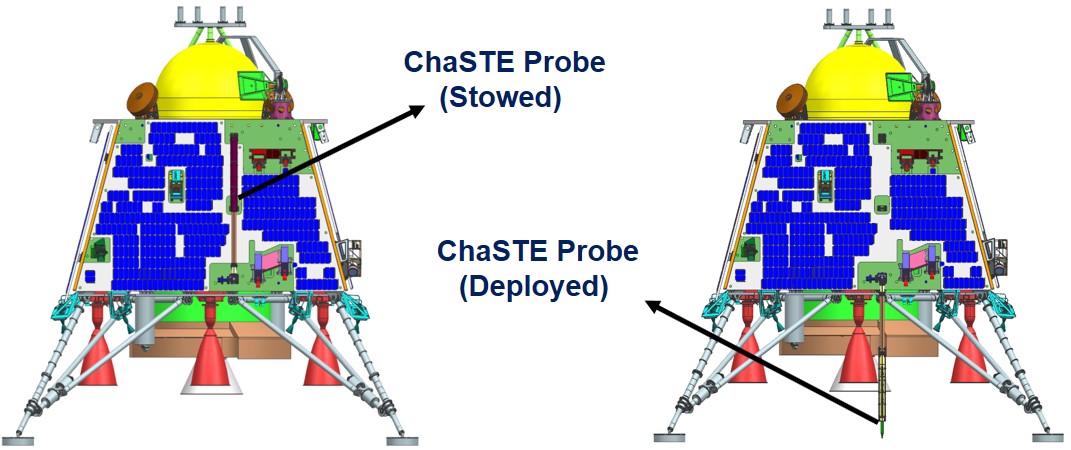 ChaSTE: First In-Situ Measurement of Surface Temperature
ChaSTE: First In-Situ Measurement of Surface Temperature Digital Child Abuse and the Dangers of AI-Based Exploitation
Digital Child Abuse and the Dangers of AI-Based Exploitation SpaceX Successfully Launches Fram2 Mission: First Human Spaceflight Over Earth’s Poles
SpaceX Successfully Launches Fram2 Mission: First Human Spaceflight Over Earth’s Poles Gaia Space Observatory: Achievements and Shutdown
Gaia Space Observatory: Achievements and Shutdown ChatGPT’s viral Studio Ghibli-style images highlight AI copyright concerns
ChatGPT’s viral Studio Ghibli-style images highlight AI copyright concerns






