
Blue Ghost became the second commercial spacecraft managed by Firefly Aerospace to successfully land on the Moon after its successful mission. The mission simultaneously connects NASA with private companies to deliver studies of the Sea of Crises. Blue Ghost achieved a successful landing in contrast to its predecessor Odysseus whose impact led to an overturned position. Experts confirm that private enterprises will lead both the expense reduction and lunar exploration advancement process.
Mission Details
-
Firefly Aerospace performed the Blue Ghost launch on January 15.
-
Targeted Sea of Crises, a lunar crater visible from Earth.
-
The vehicle achieved its intended goal of landing and it continues to operate after completing its mission unlike previous attempts made by private companies.
Significance of the Landing
-
The mission accomplished the initial fully successful autonomous lunar landing by a private organization.
-
The mission uses modern landing technology which private companies have developed to fulfill a decade-long absence since Apollo missions.
-
The establishment of robotic and human exploration at the Moon became possible through this achievement.
Role of Private Companies
-
NASA develops partnerships with commercial organizations to cut expenses.
-
The introduction of competitive commercial operations between firms will create more economical and proficient lunar mission solutions.
-
Potential for resource extraction, like water for astronauts.
Indian Context: Private Sector in Space Exploration
ISRO and Private Companies Collaboration
-
Through IN-SPACe (Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center) the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) works together with private industry entities.
-
The initiative seeks to stimulate the participation of private companies in space exploration campaigns.
Mission Similar to Blue Ghost: Vikram-S by Skyroot Aerospace
-
The introduction of Vikram-S established India as a nation with its first private space launch vehicle.
-
The launch conducted by Skyroot Aerospace using its Vikram-S space launcher was successful on November 18th 2022 under the mission Prarambh.
-
The mission demonstrated that private private sector entities can contribute effectively to space technology even though it was not a lunar exploration project.
Future Private Missions in India
-
The Agnibaan Rocket developed by Agnikul Cosmos is set to launch into orbit during 2024 as a private-sector space vehicle.
-
The Indian startup combination between Dhruva Space and Bellatrix Aerospace continues developing satellites along with propulsion solutions to explore deep outer space.
ISRO continuous support to private lunar exploration
-
ISRO announced that it intends to establish guidelines allowing private companies to participate in lunar as well as planetary missions.
-
After Chandrayaan-3's triumph Indian private enterprises became motivated to fund lunar exploration projects.
-
Private sector participation stands to gain access to Gaganyaan (India's first manned space mission) while Lubrication Resource Utilization represents another upcoming program.
Challenges & Opportunities
-
Challenges:
-
High cost of lunar exploration.
-
Advanced robotics together with radiation-protection systems need development.
-
Competition with global private space companies like SpaceX and Firefly Aerospace.
-
-
Opportunities:
-
Private lunar landers and rovers for resource extraction (e.g., water, minerals).
-
Development of low-cost launch vehicles for commercial and scientific exploration.
-
India possesses the capability to lead collaborative efforts in Artemis Accords along with global space programs.
-
Conclusion
The Blue Ghost landing represents an essential advancement in commercial outer space operations by demonstrating the ability of private companies to accomplish lunar surface operations. Adopted improvements in private-public collaboration will advance sustainable lunar exploration through facilitating human missions as well as deep space adventurations.




 India- Belgium’s Defence Cooperation in Indo-Pacific region
India- Belgium’s Defence Cooperation in Indo-Pacific region EU and India: Strengthening Ties Amidst Global Shifts
EU and India: Strengthening Ties Amidst Global Shifts Bhutan’s Strategic Role in India’s Regional Diplomacy: Budget 2025-26 Insights
Bhutan’s Strategic Role in India’s Regional Diplomacy: Budget 2025-26 Insights India-EU Strategic Partnership: Advancing Trade, Security, and Economic Cooperation
India-EU Strategic Partnership: Advancing Trade, Security, and Economic Cooperation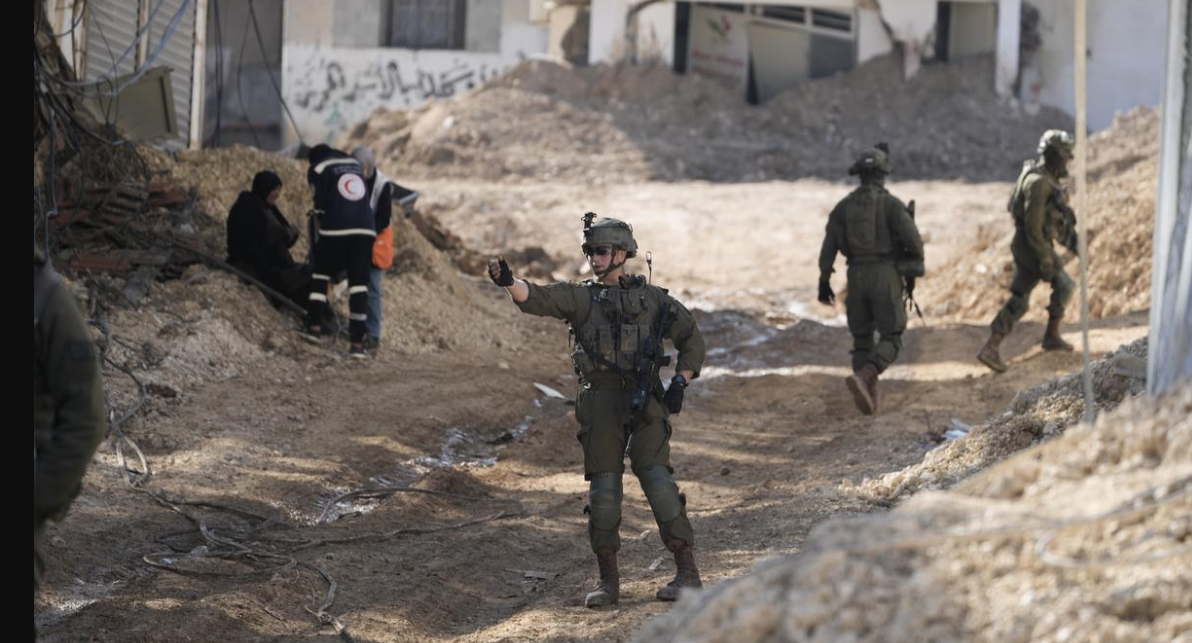 Israel Refuses to Withdraw from Gaza Corridor Amid Ceasefire Tensions
Israel Refuses to Withdraw from Gaza Corridor Amid Ceasefire Tensions India Extends Humanitarian Support to Honduras with 26 Tonnes of Disaster Relief
India Extends Humanitarian Support to Honduras with 26 Tonnes of Disaster Relief Defence Secretary Co-Chairs 13th Malaysia-India Defence Cooperation Committee Meeting
Defence Secretary Co-Chairs 13th Malaysia-India Defence Cooperation Committee Meeting India Elected to Vice Presidency of International Organization of Aids to Marine Navigation (IALA)
India Elected to Vice Presidency of International Organization of Aids to Marine Navigation (IALA) India Increases Agricultural Import Tariffs to Safeguard Farmers
India Increases Agricultural Import Tariffs to Safeguard Farmers






