
The assessment of both economic development and greenhouse gas emissions relies on carbon intensity which indicates CO₂ release based on production quantity. The evaluation takes place on various levels including the national scope and different industry sectors from steel manufacturing to medical insurance and HR service sectors. The measurement of carbon intensity has essential roles to play in the reduction of climate change impacts as well as the evaluation of different policies and fulfillment of global commitments under the Paris Agreement. China decreased its carbon intensity by 3.4% in 2024 although the target for 3.9% reduction was not achieved. Achieving net-zero emissions requires nations to minimize their carbon emissions since these efforts result in sustainable development together with climate responsibility.
Definition of Carbon Intensity
-
Economic output measurement standards depend on the amount of carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions that accompany unit production in specific industrial or national settings.
-
This metric allows organizations along with nations to determine their economic growth rate while achieving effective carbon emission control.
Sector-Specific Measurement
-
Steel manufacturers measure their operations through steel production that rises with decreasing CO₂ emissions.
-
Success claims processed within medical insurance operations result in specific carbon dioxide emissions.
-
HR Services → Carbon emissions per unit of productivity improvement.
-
The measurement seeks to calculate capita GDP growth against CO2 emissions at the national level.
Global Relevance of Carbon Intensity
-
Measuring carbon intensity represents a vital tool for dealing with climate change and building an economy based on low-carbon operation.
-
The measurement lets authorities monitor emission changes on a national and industrial scale.
-
The tracking of international climate commitment progress occurs through its implementation including the Paris Agreement and Net-Zero targets.
Recent Example: China’s Carbon Intensity
-
The carbon intensity in China decreased by 3.4% in 2024 although the country missed its original 3.9% target.
-
The reduction of 3.4% represents a critical step because China has set a goal to reach carbon emission peak before 2030.
-
Multiple experts warn that reaching this goal faces difficulty because China needs coal for power and continues experiencing quick economic progress.
Conclusion
Carbon intensity functions as a fundamental performance indicator for organizations to strike optimal economic progress and environmental stewardship. Countries together with industries need to work on lowering their carbon intensity levels because it will help achieve worldwide sustainability targets along with minimizing climate change consequences.



 Why Protecting the Aravalli Range Matters for Climate, Water, and Biodiversity
Why Protecting the Aravalli Range Matters for Climate, Water, and Biodiversity Supriya Sahu Wins UNEP Champions of the Earth 2025
Supriya Sahu Wins UNEP Champions of the Earth 2025 World Soil Day 2025: Celebrating “Healthy Soils for Healthy Cities”
World Soil Day 2025: Celebrating “Healthy Soils for Healthy Cities”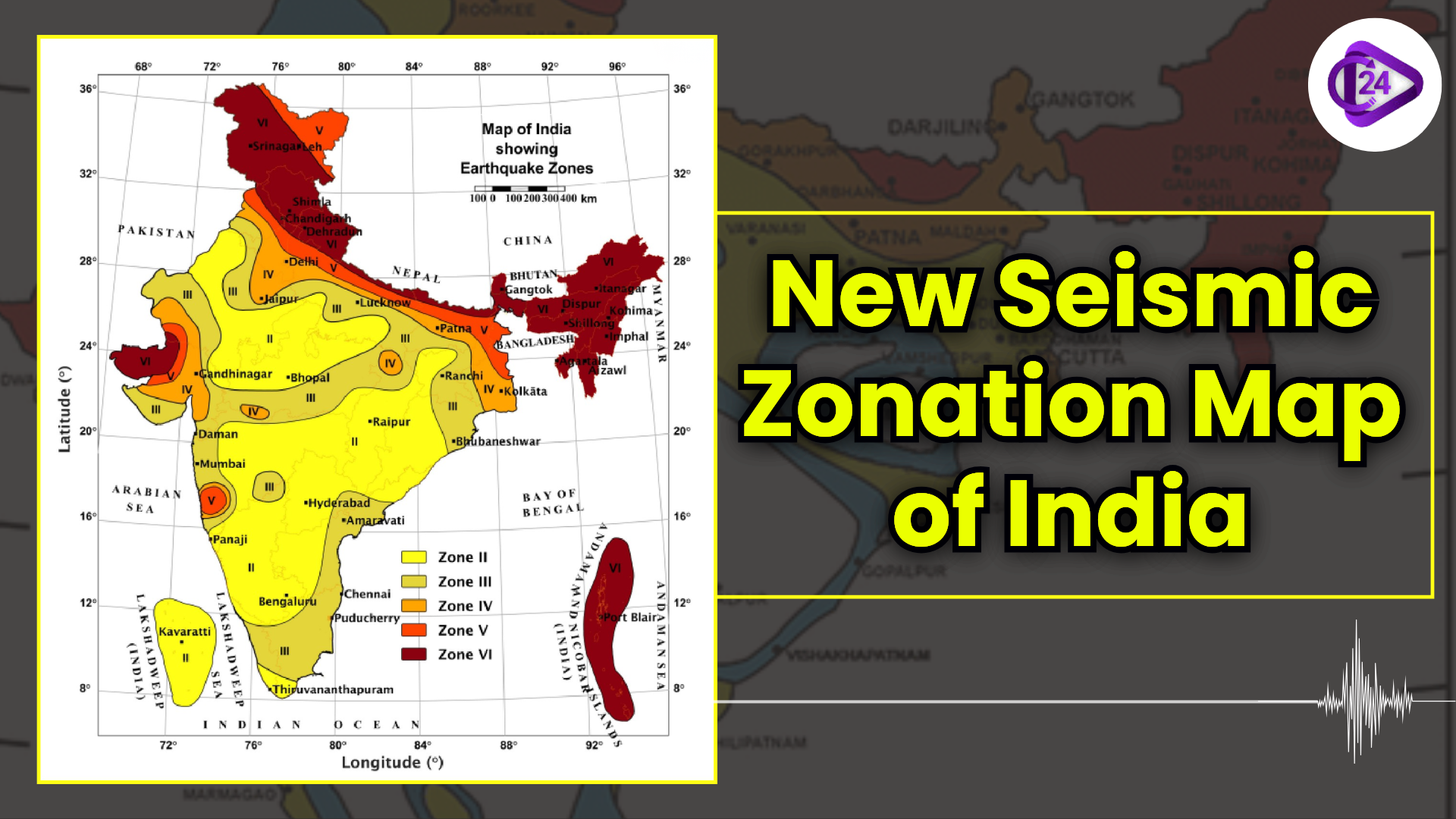 New Seismic Zonation Map of India
New Seismic Zonation Map of India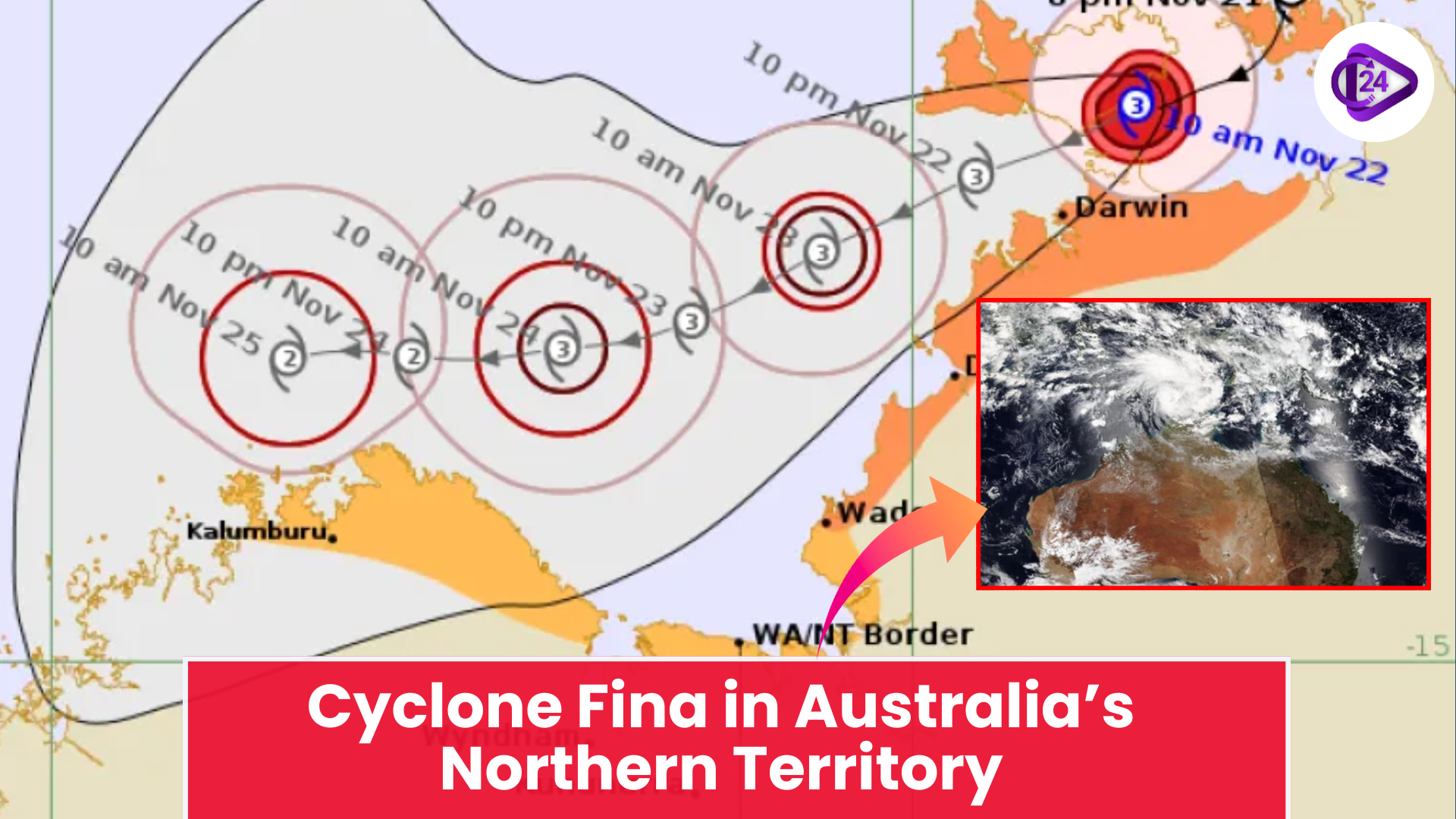 Cyclone Fina Hits Northern Australia With Destructive Force
Cyclone Fina Hits Northern Australia With Destructive Force Tiger Returns to Gujarat After 32 Years | Historic Wildlife Comeback 2025
Tiger Returns to Gujarat After 32 Years | Historic Wildlife Comeback 2025 Namdapha Butterfly Festival Showcases the Wild Heart of Arunachal Pradesh
Namdapha Butterfly Festival Showcases the Wild Heart of Arunachal Pradesh Gogabeel Lake Achieves Ramsar Status for Biodiversity and Conservation
Gogabeel Lake Achieves Ramsar Status for Biodiversity and Conservation Cyclone Montha Makes Landfall Near Kakinada, Bringing Destruction to Andhra and Odisha
Cyclone Montha Makes Landfall Near Kakinada, Bringing Destruction to Andhra and Odisha India Conducts First-Ever DNA-Based Elephant Census, Reveals Population Decline by 25%
India Conducts First-Ever DNA-Based Elephant Census, Reveals Population Decline by 25%






