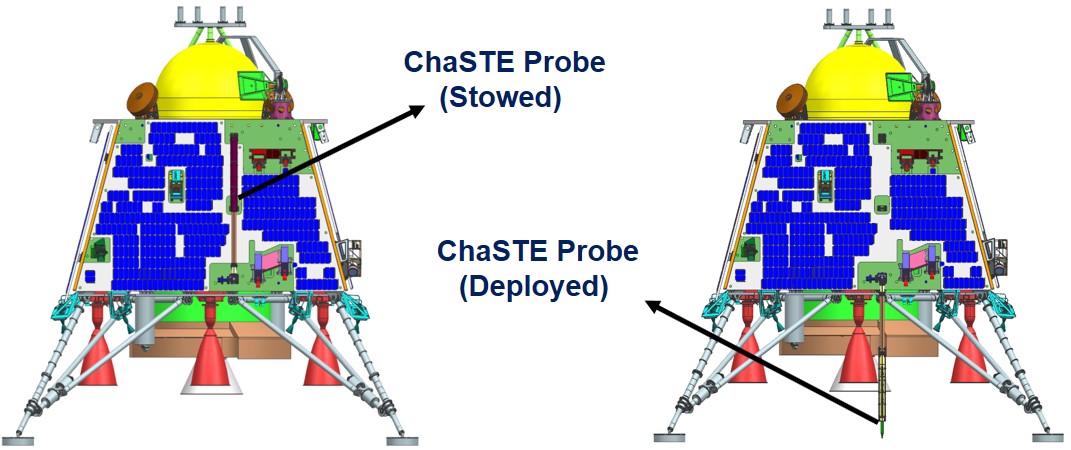
The Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment (ChaSTE) component of Chandrayaan-3 has successfully collected crucial thermal data about high-latitude lunar surfaces. The latest achievement enables researchers to understand lunar surface features and ice moisture distribution which are fundamental for human operations on the moon. The Vikram lander’s instruments including ChaSTE helps researchers measure ambient temperatures of lunar surface locations near the Moon’s southern region.
-
This mission conducted the first ever subsurface soil penetration of celestial matter followed by the deployment of an in-situ thermal probe for temperature measurements.
-
The probe contains 10 distributed temperature sensors that extend 1 cm apart on its entire length.
-
The probe entered lunar soil through a deployment system that relied on rotating movements.
-
Throughout Chandrayaan-3 mission duration (1 lunar day) the probe descended to its bottom limit of 10 cm to gather scientific data.
Key Observations
-
The Shiv Shakti landing site measured 355 K (82°C) surface temperature as the maximum value which exceeded earlier predictions of 330 K by 25 K.
-
The study discovered that temperatures in polar lunar areas display substantial spatial variations unlike the steady conditions prevailing at equatorial areas.
-
The collected data from the ChaSTE instrument provides evidence that lunar water-ice deposits exist in higher concentrations than scientists had earlier estimated.
-
The discovery of water-ice stands as essential for lunar resource utilization throughout human settlement and additional space exploration operations.
Conclusion
The ability of ChaSTE to directly measure lunar surface temperatures represents a major achievement in lunar research development. The recorded observations will enhance lunar thermophysical property knowledge as well as guide programs aiming to establish human settlements and utilize lunar resources. The successful accomplishment of Chandrayaan-3 enables scientists to develop advanced methods for future lunar exploration as well as(resource) management on the Moon.



 IIA Achieves Breakthrough in Measuring Helium Abundance in the Sun
IIA Achieves Breakthrough in Measuring Helium Abundance in the Sun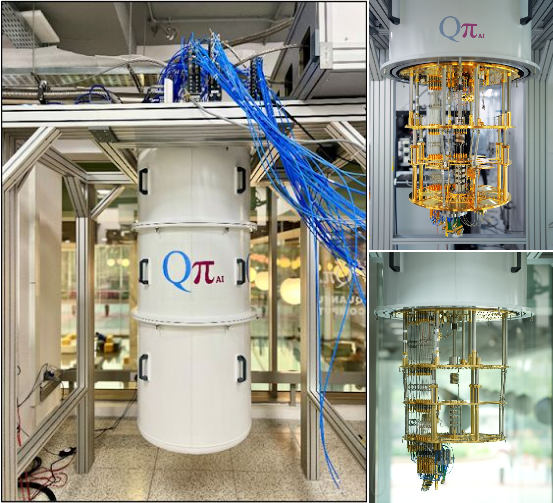 QpiAI Launches India’s First Full-Stack Quantum Computer, QpiAI-Indus, on World Quantum Day
QpiAI Launches India’s First Full-Stack Quantum Computer, QpiAI-Indus, on World Quantum Day ISRO to Send Tardigrades on Axiom-4 Mission: A Step Towards Advancing Space Research
ISRO to Send Tardigrades on Axiom-4 Mission: A Step Towards Advancing Space Research TERI's Nano Sulphur Breakthrough in Mustard Cultivation
TERI's Nano Sulphur Breakthrough in Mustard Cultivation ISRO's Successful Second Docking of Satellites – A Milestone in Space Technology
ISRO's Successful Second Docking of Satellites – A Milestone in Space Technology Potential Biosignatures Discovered on Exoplanet K2-18b by JWST
Potential Biosignatures Discovered on Exoplanet K2-18b by JWST India Launches First Native Seed Germination Database for Ecological Restoration
India Launches First Native Seed Germination Database for Ecological Restoration India’s Evolving Approach to Artificial Intelligence Governance and Regulation
India’s Evolving Approach to Artificial Intelligence Governance and Regulation Golden Jubilee of Aryabhata 2025: Celebrating India’s First Satellite and ISRO’s Historic Milestone
Golden Jubilee of Aryabhata 2025: Celebrating India’s First Satellite and ISRO’s Historic Milestone ESA's Biomass Mission 2025: Tracking Global Forest Carbon Storage via Satellite
ESA's Biomass Mission 2025: Tracking Global Forest Carbon Storage via Satellite






