The FSSAI of the country aims at paving way for the regulation on lab-grown meat, dairy and egg through the preparation of a regulation. It is a step India takes up to capture a share of the fast-growing global market of organic, and ethical non-hazardous food substitute in the biotechnology industry and environmental conservation.
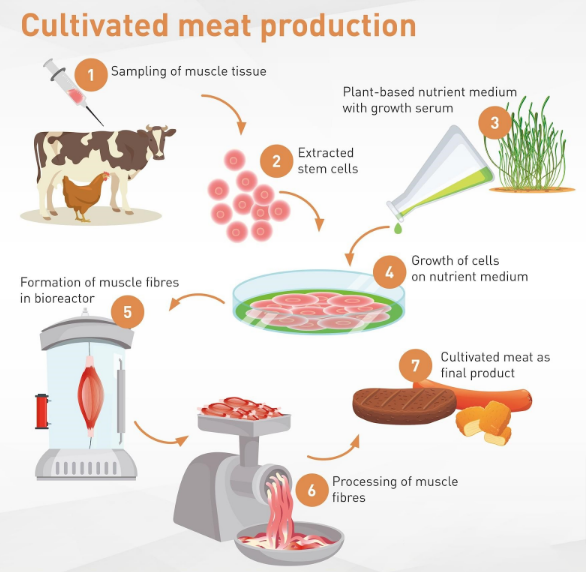
Understanding Laboratory-Grown Meat: The meats of concern here are laboratory grown meat or known as cultured or cultivated meats, these are tissues acquired from living animals or fertilized eggs that are then cultured artificially. It is different from ordinary meat since it does not need to kill animals for the food to be prepared, and therefore requires using more ethical unobjectionable production methods. Plant based meat, on the other hand, has similar structure, flavor and color to actual animal meat using ingredients such as grains, pulses and plant derived oils in its formulation, but is suitable for vegans.
Significance of the Regulatory Framework: At the moment, India does not have any restrictions for lab grown or fermentation derived proteins but it does have rules for plant proteins. The new framework is intended to fill this void and reassure stakeholders as they seek to detail the necessary guidelines to allow for the development and growth of this relatively new industry.
Economic Implications: The size of meat market involving animal products exports from India is remarkable with the exporting value of 4.5 billion USD in 2023-24. According to the sector of animal type consumed, the largest share was taken by buffalo meat while poultry and sheep/goat meat were the other major shares. Labelling and releasing cultured meat could potentially expand the food portfolio of operations in India and bring down continued reliance on extensive animal farming, which even though provides fiscal benefits is an environmentally pressurising method.
Sustainability Goals: The move is in accordance with India’s decision to provide food security and cutting back on emissions through animal grazing. Currently, there is a need to come with ways of producing meat that shall help in satisfying growing demand for proteins without affecting the environment destructively through issues such as deforestation, water use as well as methane emission.
Opportunities for Biotechnology: This regulation framework is a key factor in opening opportunities for upgrading the innovations within the biotechnology and food sciences sectors in India. They could foster investments, encourage R & D activities & build India as a global hub in sustainable food technology. Through this innovation, India can play an important role of supporting the global quest for finding real and meaningful solutions in the fight against food insecurity and sustainable consumption.
Conclusion: FSSAI’s attempt to streamline lab-grown meat is another positive step towards the disaggregation of the Indian food sector. Managing sustainability, ethical and economic objectives aligns it to the primary question of SSC and UPSC syllabi, which aspiring officers ought to grasp. It also demonstrated India’s ability to embrace international trends and the importance of the rapid-growing regulatory authorities in a world that requires the formulation of policies create new opportunities for innovative products which at the same time can also protect the public and the environment.










