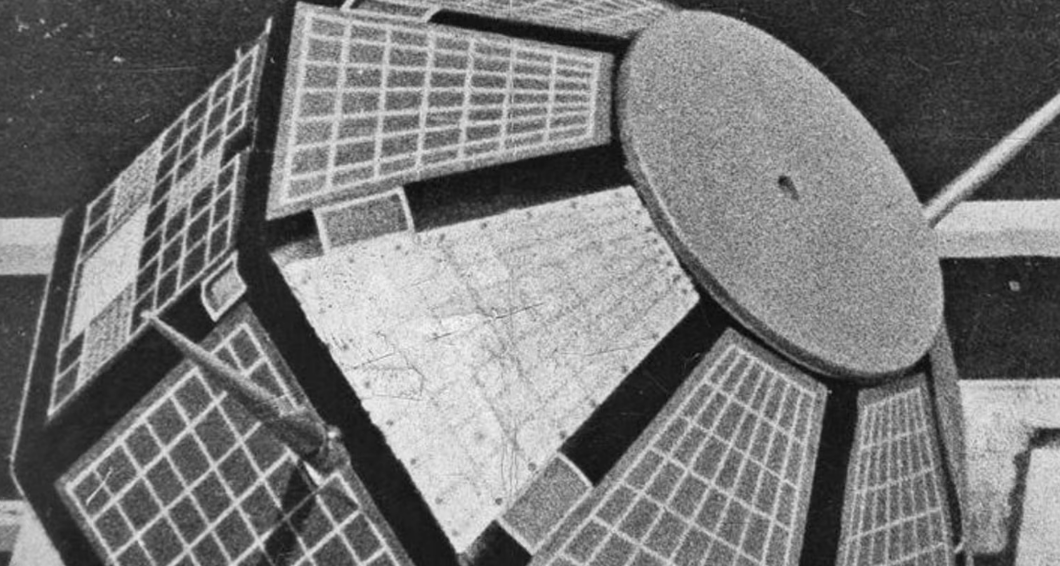
India’s pioneering satellite Aryabhata reached orbit fifty years ago on April 19, 2025. Aryabhata found its launch destination in the Soviet Union in 1975 as the flagship mission for India's new space exploration venture under the oversight of ISRO. India’s membership in the spacefaring nations alongside satellite technology and space exploration developments began with the seminal Aryabhata mission.
Historical Significance:
-
Aryabhata was launched on April 19, 1975, aboard a Soviet Kosmos-3M rocket from Kapustin Yar, USSR
-
Aryabhata positioned India as the 11th nation worldwide that launched satellites into orbit.
-
This accomplished launch set the first chapter of India's space technology exploration and research activities.
Naming of Aryabhata:
-
Prime Minister Indira Gandhi made her selection from among three Potential Names: Aryabhata, Mitra, and Jawahar.
-
Aryabhata received its name from the Indian astronomer and mathematician who lived during the ancient period.
-
The satellite received two alternate names as Jawahar and Mitra which conveyed both Indian freedom along with Soviet-Indian friendship.
Technical and Design Aspects:
-
Aryabhata featured 26 flat surfaces with a 1.59 meter diameter and 1.19 meter height in its quasi-spherical shape.
-
The spacecraft used 36,800 sq cm worth of solar cells to produce a maximum power output of 46 watts.
-
The orbit maintained by the satellite reached 563 km x 619 km heights.
Mission Objectives and Performance:
-
Aryabhata conducted scientific research for X-ray astronomy as well as aeronomy and solar physics studies while maintaining its experimental objectives.
-
The power distribution problem during initial operations let only one of the payloads function.
-
Aryabhata transmitted signals until February 10, 1992 before the mission ended after 17 years of successful operation.
Legacy and Impact:
-
Through giving confidence to ISRO Aryabhata paved the way for a serious Indian space technology program.
-
India has established 131 satellites while maintaining 55 operational satellites in space since its initial space project.
-
By launching 433 satellites for 34 countries the Indian space program delivered support for global missions after its establishment.
Golden Jubilee Celebrations:
-
The organization ISRO will organize unique programs to mark this historic event.
-
Through the jubilee event India celebrates its transformation from beginning space missions to becoming a worldwide space leadership force.
Conclusion:
Aryabhata’s launch in 1975 achieved status beyond technology because it demonstrated India’s scientific ambitions and accomplishment capabilities. This 50-year anniversary of Aryabhata’s achievement functions as a milestone which represents Indian innovation alongside national determination and patriotic pride. Through its launch India gained control over its space exploration capabilities thus creating a thriving space economy which positioned the nation as a prominent global space power.


 India Launches First Native Seed Germination Database for Ecological Restoration
India Launches First Native Seed Germination Database for Ecological Restoration India’s Evolving Approach to Artificial Intelligence Governance and Regulation
India’s Evolving Approach to Artificial Intelligence Governance and Regulation ESA's Biomass Mission 2025: Tracking Global Forest Carbon Storage via Satellite
ESA's Biomass Mission 2025: Tracking Global Forest Carbon Storage via Satellite ChaSTE: First In-Situ Measurement of Surface Temperature
ChaSTE: First In-Situ Measurement of Surface Temperature Digital Child Abuse and the Dangers of AI-Based Exploitation
Digital Child Abuse and the Dangers of AI-Based Exploitation SpaceX Successfully Launches Fram2 Mission: First Human Spaceflight Over Earth’s Poles
SpaceX Successfully Launches Fram2 Mission: First Human Spaceflight Over Earth’s Poles Gaia Space Observatory: Achievements and Shutdown
Gaia Space Observatory: Achievements and Shutdown ChatGPT’s viral Studio Ghibli-style images highlight AI copyright concerns
ChatGPT’s viral Studio Ghibli-style images highlight AI copyright concerns Bellatrix Aerospace Partners with Astroscale Japan for Space Debris Removal
Bellatrix Aerospace Partners with Astroscale Japan for Space Debris Removal






