
The worldwide effort to regulate Artificial Intelligence faces distinct approaches between countries that result from their socio-economic and political backgrounds. India opts for mission-based development instead of standardized legal and strategic frameworks when approaching Artificial Intelligence governance and lawmaking. India's initiatives support adaptability to emerging technologies yet the country lacks official AI strategy or regulation which creates uncertainty about responsibility and accessibility together with ethical AI utilization and readiness. India can develop an equitable and sustainable AI policy through global benchmarking and utilization of the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023 to define its AI integration strategies.
Context:
-
Global Trends: Global trends show that numerous countries created AI strategy documents together with AI laws to support ethical development of inclusive AI systems.
-
India’s position: India operates without an established AI law while using both the IndiaAI mission and advisory bodies along with no formal strategy.
-
Policy Gap: The current Indian approach is flexible yet it has no defined goals and measurable targets and does not establish accountability frameworks.
-
Urgency for regulation: Restrained AI adoption across critical sectors requires India to build official regulations as well as commence discussions about AI governance.
Key Points:
Global Regulatory Landscape:
-
AI-specific laws now exist in the EU, China and Canada as well as other nations.
-
More than 85 international nations together with the African Union have created official AI strategy documents.
-
The United States uses a divided-by-sectors system while the EU implements its governance through central control.
India’s Current Approach:
-
Indian institutions have yet to introduce approved national AI legislation or strategic guidelines from the government.
-
The 2018 AI strategy developed by NITI Aayog has not been executed yet.
-
The IndiaAI mission stimulates innovation through a seven-pillar organizational system.
-
Special expert groups composed of advisors have been developing initial governance recommendations.
Advantages of India’s Approach:
-
India has the capability to change and respond to new technological developments along with international relations and economic shifts.
Limitations and Risks:
-
Lack of clarity on national vision, implementation, and accountability.
-
Absence of public engagement and transparent algorithmic use, especially in public services.
-
Risk of reactive policy-making and dependence on leadership continuity.
-
AI technologies pose three particular dangers which include the production of fake information alongside privacy violation and biased practices.
Comparative Lessons from Abroad:
-
The DPDP Act in India follows the EU GDPR concept by establishing central authority and targeting all sectors with their provisions.
-
China implements specific laws to regulate deep synthesis systems together with generated content created by artificial intelligence technology.
-
The establishment of a hybrid model should utilize India's foundational structure of digital data protection to enhance its potential performance.
A structured AI policy required:
-
India must establish a precise declaration about its future outlook for Artificial Intelligence development.
-
The establishment of capacity development together with infrastructural improvements should include ethical guidelines.
-
The initiative should focus on selecting crucial sectors which include healthcare together with agriculture and education.
-
The policy should establish which authorities will oversee enforcement and responsibilities.
-
The public needs to engage in dialogue about AI issues with their government and citizens.
Conclusion
The time is now for India to develop its framework regarding Artificial Intelligence governance. The polycentric approach of mission-focused development helps India adapt to technological changes but leaves space for doubts about responsibility and ethical practices and public trust in AI applications. India should define a complete AI policy now because artificial intelligence will strongly incorporate itself into key industrial applications.


 Potential Biosignatures Discovered on Exoplanet K2-18b by JWST
Potential Biosignatures Discovered on Exoplanet K2-18b by JWST India Launches First Native Seed Germination Database for Ecological Restoration
India Launches First Native Seed Germination Database for Ecological Restoration Golden Jubilee of Aryabhata 2025: Celebrating India’s First Satellite and ISRO’s Historic Milestone
Golden Jubilee of Aryabhata 2025: Celebrating India’s First Satellite and ISRO’s Historic Milestone ESA's Biomass Mission 2025: Tracking Global Forest Carbon Storage via Satellite
ESA's Biomass Mission 2025: Tracking Global Forest Carbon Storage via Satellite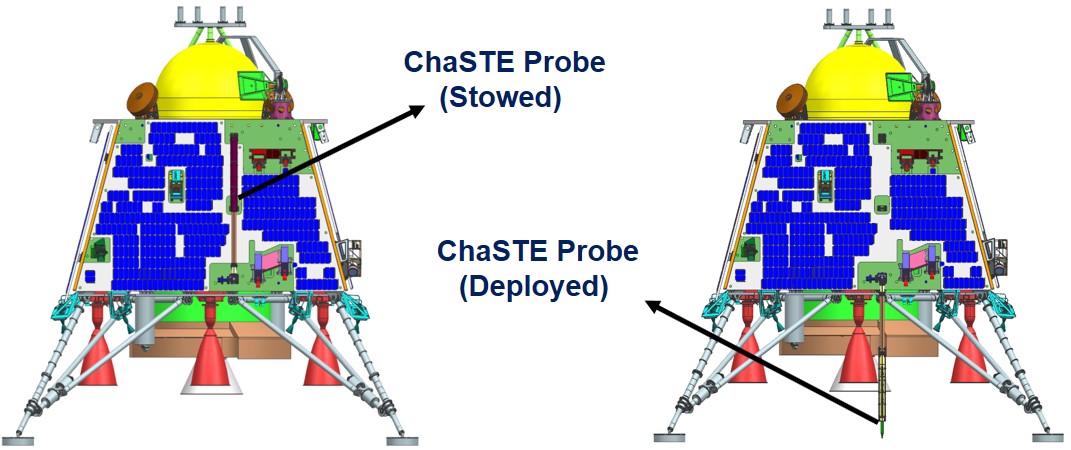 ChaSTE: First In-Situ Measurement of Surface Temperature
ChaSTE: First In-Situ Measurement of Surface Temperature Digital Child Abuse and the Dangers of AI-Based Exploitation
Digital Child Abuse and the Dangers of AI-Based Exploitation SpaceX Successfully Launches Fram2 Mission: First Human Spaceflight Over Earth’s Poles
SpaceX Successfully Launches Fram2 Mission: First Human Spaceflight Over Earth’s Poles Gaia Space Observatory: Achievements and Shutdown
Gaia Space Observatory: Achievements and Shutdown ChatGPT’s viral Studio Ghibli-style images highlight AI copyright concerns
ChatGPT’s viral Studio Ghibli-style images highlight AI copyright concerns






