
India’s measures towards environmental conservation are already paying a positive of foreseen impacts as seen in the latest report of State of Forest in India – 2023. The country’s Forest and Tree Cover now covers twenty-five point one seven (25.17) % of the total land area, and forest cover has expanded to seven hundred and fifteen (715, 343) sq kilometers in 2023. He pointed out that fire incidents have been reduced by about two-thirds based on the same data as well as other authorities. These innovations are helping India in meeting its NDC goals of developing carbon sink worth 2.5 – 3.0 billion tones by 2030.
National-level programmes are Green India Mission, Nagar Van Yojana and Mangrove Initiative for Sustainable Technology for Implementation MISHTI. CAMPA and School Nursery Yojana are other related legal bearing programs that encourage sustainable forest management.
Rain makers like Tulsi Gowda are examples of how one persons effort can bring life change. This paper highlights India’s balanced approach to ensuring development and conservation, and therefore its commitment to a better environment.
Key Points
-
According to the India State of Forest Report (ISFR) 2023, India has a total Forest and Tree Cover of 827,357 sq.km; constituting 25.17% of its area.
-
Exclusive of forest cover, it occupies 715,343 sq km and of trees cover only 112,014 sq km.
-
Between 2013 and 2023, the area under forest also raised from 698,712 sq. km to 715,343 sq. km.
-
Fire cases have reduced, from 223,333 hotspots in the year 2021-22, to 203,544 hotspots in the year 2023-24.
Climate Change Influence and Carbon Storage
-
India boasts a carbon sink of 30.43 billion tonnes of CO₂ equivalent, and is close to reaching its NDC’s proposed target of 2.5-3.0 billion tonnes for 2030.
Key Government Initiatives
-
National Mission for a Green India (GIM):
-
Getting its start in 2014, the initiative began by exclusively targeting forests for protection, restoration, and future development.
-
To 17 states and 1 UT across ₹944.48 crore has been allocated, at prescribed state-wise percentage split as advised.
-
-
Nagar Van Yojana (NVY):
-
Green growth projects, the budget of ₹431.77 crore has been included towards the funding of 546 projects spread over 31 states/UT.
-
-
School Nursery Yojana (SNY):
-
Promoting tree planting among school children; a total of ₹4.80 crore has been earmarked for this purpose and disbursed in 19 states and Union Territories.
-
-
Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats & Tangible Incomes (MISHTI):
-
Mangrove conservation project spread over five years with ₹17.96 crore earmarked for major coastal states and UTs.
-
-
Compensatory Afforestation Fund (CAMPA):
-
Ensures that forest loss resulting from other non-forest use is addressed by paying for the production of those other goods and services, and restoring the degraded ecosystems.
-
-
Afforestation Targets and Mass Campaigns:
-
This involvement is elated by activities such as Van Mahotsav, Wildlife Week, propositions for green campaigns and friendly drives.
-
Legal Provisions
-
Indian Forest Act, 1927
-
Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972
-
Van Sanrakshan Evam Samvardhan Adhiniyam 1980
-
The implementation is the actual task of State Governments and UTs for enforcing the provisions of the conservation laws & orders passed by the Courts.
Community Involvement and Inspirational Efforts
-
Environmental conservation is not a policy only. There are ordinary people like Padma Shri Tulsi Gowda popularly known as ‘Mother of Trees,’ who has planted lakhs of trees and built forests.
-
The life of Tulsi Gowda is an example of the power of people joining an organized system to fight for a green environment.
Conclusion
India directs development with the significant goal to preserve the environment based on the examples of the green recovery. ISFR 2023 paints a positive picture of the country with regard to the manner in which forest cover is being increased, fire incidents and ecosystem. Structure: India has put into practice strong polices and community participation for cleaner, healthier and green environment for better and sustainable future in future generations.



 Why Protecting the Aravalli Range Matters for Climate, Water, and Biodiversity
Why Protecting the Aravalli Range Matters for Climate, Water, and Biodiversity Supriya Sahu Wins UNEP Champions of the Earth 2025
Supriya Sahu Wins UNEP Champions of the Earth 2025 World Soil Day 2025: Celebrating “Healthy Soils for Healthy Cities”
World Soil Day 2025: Celebrating “Healthy Soils for Healthy Cities”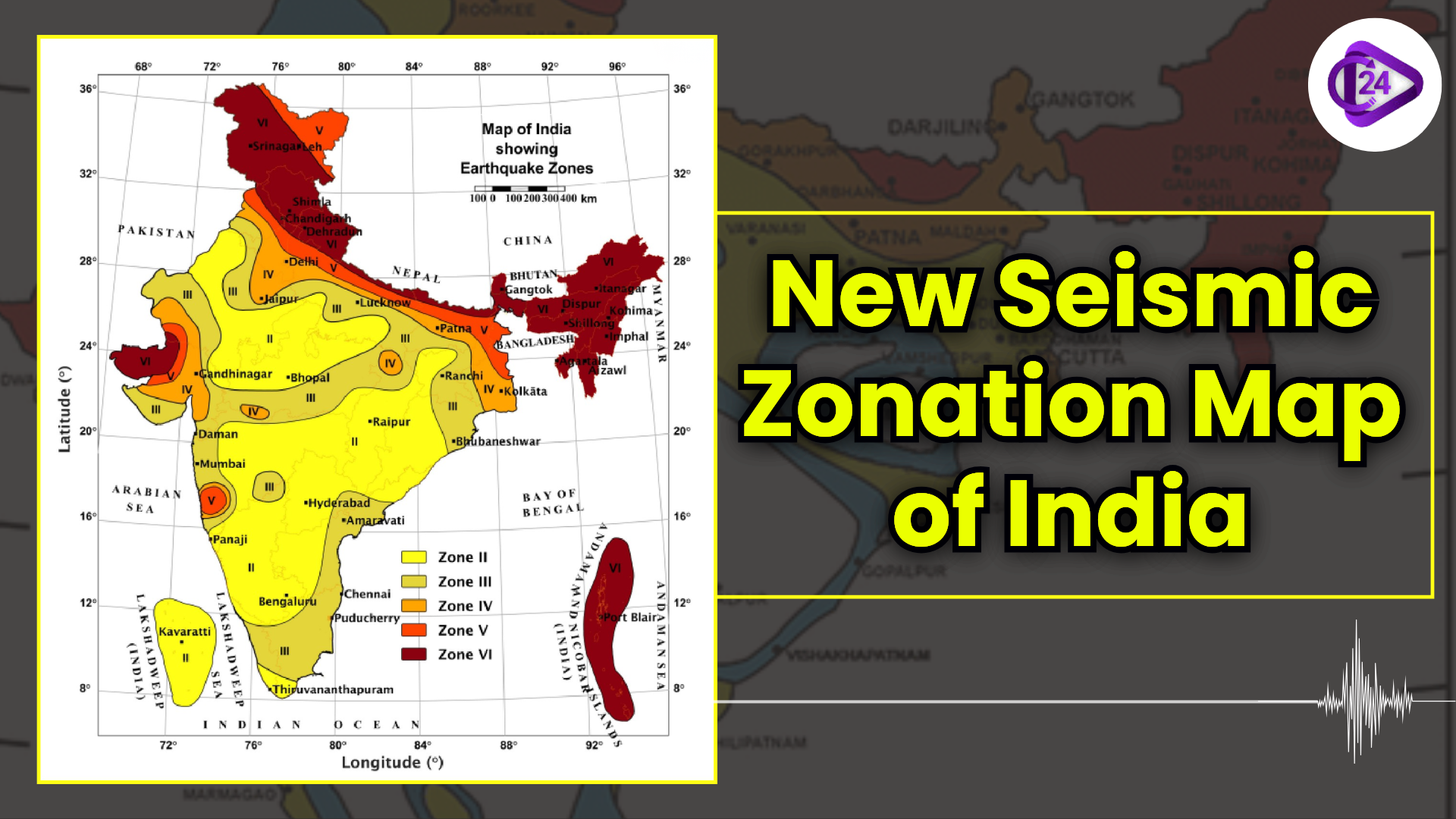 New Seismic Zonation Map of India
New Seismic Zonation Map of India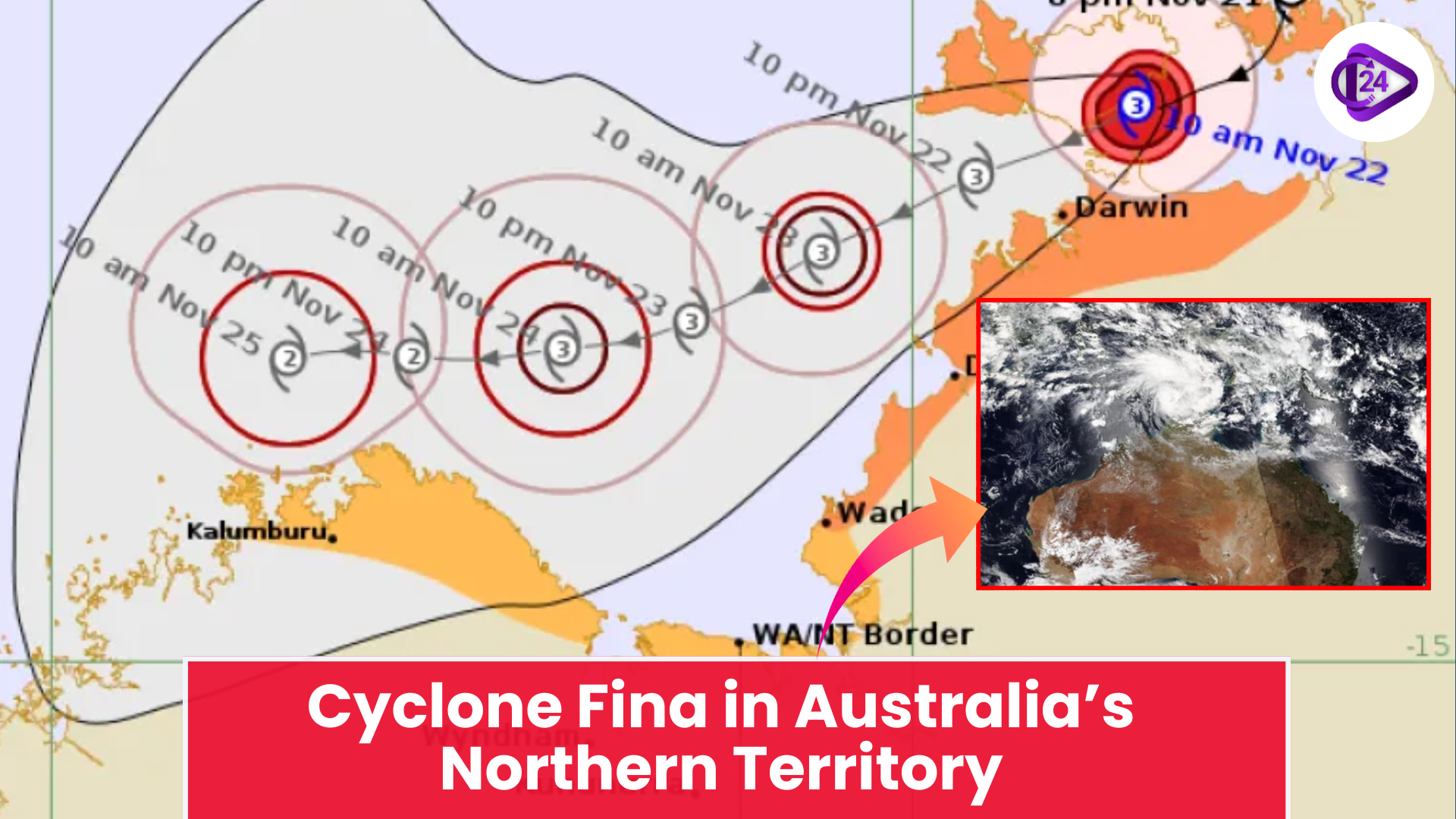 Cyclone Fina Hits Northern Australia With Destructive Force
Cyclone Fina Hits Northern Australia With Destructive Force Tiger Returns to Gujarat After 32 Years | Historic Wildlife Comeback 2025
Tiger Returns to Gujarat After 32 Years | Historic Wildlife Comeback 2025 Namdapha Butterfly Festival Showcases the Wild Heart of Arunachal Pradesh
Namdapha Butterfly Festival Showcases the Wild Heart of Arunachal Pradesh Gogabeel Lake Achieves Ramsar Status for Biodiversity and Conservation
Gogabeel Lake Achieves Ramsar Status for Biodiversity and Conservation Cyclone Montha Makes Landfall Near Kakinada, Bringing Destruction to Andhra and Odisha
Cyclone Montha Makes Landfall Near Kakinada, Bringing Destruction to Andhra and Odisha India Conducts First-Ever DNA-Based Elephant Census, Reveals Population Decline by 25%
India Conducts First-Ever DNA-Based Elephant Census, Reveals Population Decline by 25%






