
India’s Finance Ministry has proposed updating the GDP base year from 2011-12 to 2022-23. This revision aims to capture recent structural changes like digitization, emerging industries, and post-pandemic economic shifts. It ensures more accurate policy implementation and alignment with global standards. By using 2022-23 data, India can reflect its current economic realities and enhance the relevance of statistical benchmarks. This move strengthens evidence-based policymaking.
What is the base year?
A base year is a year that is used to measure other economic factors such as gross domestic product. It is usually given the arbitrary benchmark value of 100, against which fluctuations in economic activities, prices ,and other important indicators are measured. This index is also used for adjustment for inflation while making a comparison of price level in different periods since it standardised the value of a selected basket of commodities in the base year.
Why Update the Base Year?
-
Economic Relevance:
-
The base year 2011-12 therefore does not capture the recent structural changes in the economy such as digitization, new industries, or post- COVID-19 adjustments.
-
Using data up to 2022-23 is useful in that it captures current levels of GDP in relation to current levels of consumption, and contributions from industries.
-
-
Policy Formulation:
-
Policy decisions made based on stale data do not reflect the economic environment and hence are biased.
-
Improved data offer an opportunity based on evidence policymaking.
-
-
Global Alignment:
-
Actually, it aligns Indian GDP computations with globally recognised systems and such factors as the CPI and WPI.
-
Implications of the Update
-
Revision of Historical GDP Figures:
-
Old growth rates will be averaged to present a more coherent picture of the economical tendencies.
-
-
Improved Policy Planning:
-
It gets to formulate specific economic policies with the help of better statistics.
-
-
Alignment with Indices:
-
This applies the update to maintain comparable relevancy with other economic indicators thereby improving the reliability of the data.
-
Status of the Revision
-
There is one MoSPI constituted a 26-member Advisory committee on National Accounts Statistics which is headed by Biswanath Goldar.
-
This committee has the responsibility of putting to finality the new base year in relation to GDP figures and the indices.
GDP Calculation in India
India employs two primary methods to calculate GDP:
-
Factor Cost Method:
-
Assesses the performance of major industries in areas such as agriculture, mining and manufacturing, utilities, trade and public administration.
-
A key financial metric that estimates the total value change delivered by these sectors.
-
-
Expenditure Method:
-
In other words, it examines household consumption expenditure on final consumption goods and services.
-
The four sectors that have been taken into account include: Consumption expenditures of households, Investments, Government spending, and Net exports.
-
These two methods were used to give a comprehensive view of the economy from two tactical angles as mentioned earlier.
Data Collection Process
-
The macroeconomic data for GDP computations are collected by the Central Statistics Office (CSO) under MoSPI.
-
It also annually carries out polls and has production indicators like the IPI and the CPI alongside state and federal agencies.
Conclusion
This transition to base year 2022-23 for industrial production methodology substantially explains India’s consistent efforts towards refining its economic database. This update will further enhance validity of GDP figures as measures of economic performance and reference points for development policies in view of the changing economic landscape.



 India and Oman Sign the Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA)
India and Oman Sign the Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) RBI Retains SBI, HDFC Bank, and ICICI Bank as Domestic Systemically Important Banks
RBI Retains SBI, HDFC Bank, and ICICI Bank as Domestic Systemically Important Banks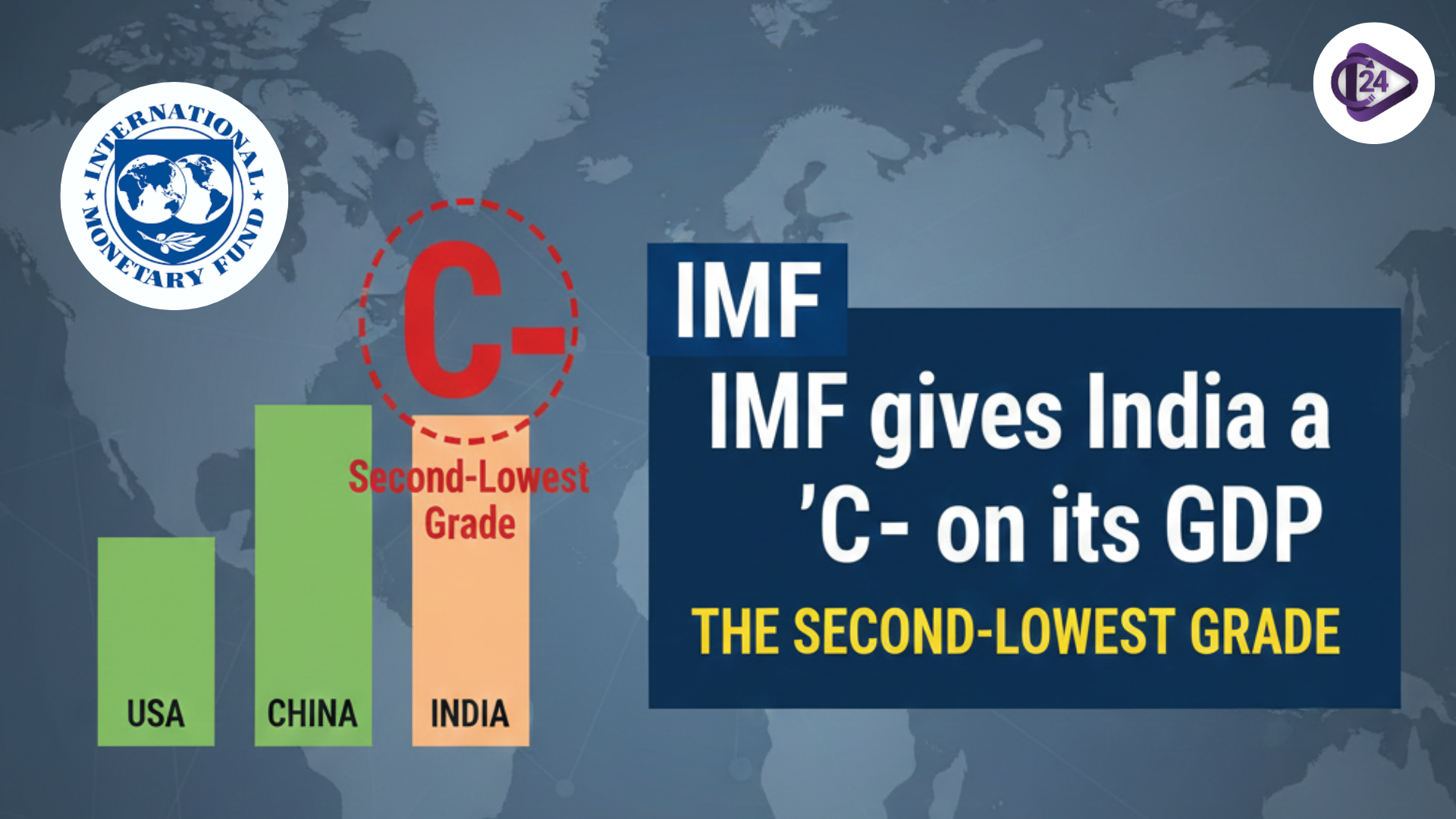 IMF gives India a ‘C’ on its GDP and other national accounts data, the second-lowest grade
IMF gives India a ‘C’ on its GDP and other national accounts data, the second-lowest grade India Witnesses Rapid Surge in Ultra-Processed Food Consumption
India Witnesses Rapid Surge in Ultra-Processed Food Consumption HDFC Bank Secures the Top Rank in India’s 2025 Brand Value Index
HDFC Bank Secures the Top Rank in India’s 2025 Brand Value Index ASSOCHAM New President Nirmal Minda to Drive Industrial Innovation and Sustainability in India
ASSOCHAM New President Nirmal Minda to Drive Industrial Innovation and Sustainability in India 8th Pay Commission 2025: Latest News, Salary Hike & DA Update
8th Pay Commission 2025: Latest News, Salary Hike & DA Update Sonali Sen Gupta Takes Charge as RBI Executive Director
Sonali Sen Gupta Takes Charge as RBI Executive Director Shram Shakti Niti 2025: India’s Future-Ready Labour Policy for Employment Growth
Shram Shakti Niti 2025: India’s Future-Ready Labour Policy for Employment Growth Secure UPI Transactions: RBI and NPCI Introduce Biometric Authentication
Secure UPI Transactions: RBI and NPCI Introduce Biometric Authentication






