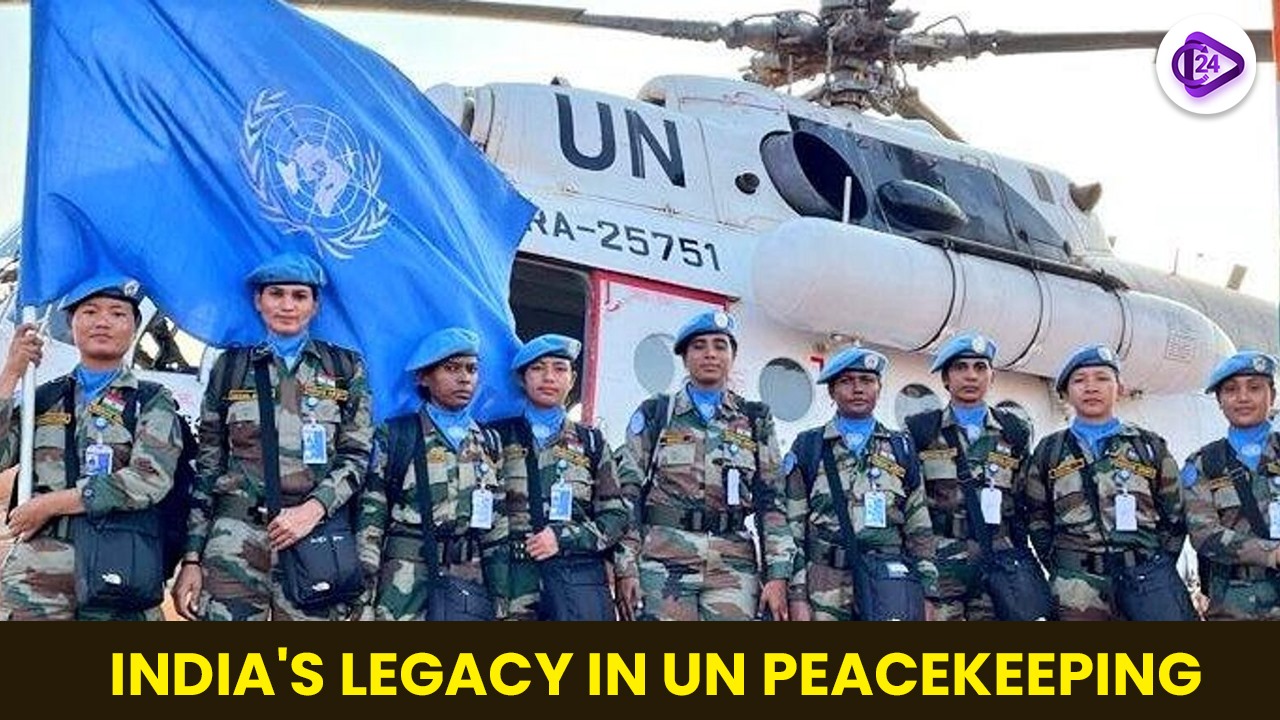

The United Nations has acknowledged India as its cornerstone force which supplied over 290,000 troops for using more than 50 peacekeeping missions across the world. The country of India stands among the biggest military contributors to United Nations peacekeeping missions which currently maintain over 5,000 troops in nine operational missions.
The “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam” principle of India supports its peacekeeping doctrine by emphasizing worldwide networks of diplomatic dialogue and cooperative action at the heart of peace operations. Military together with humanitarian support and political stabilization constitutes the essential missions where Indian peacekeeping forces demonstrate their effectiveness.
Women peacekeepers serving India have successfully eliminated gender-related barriers to boost both gender balance and operational achievements in their missions. The Centre for United Nations Peacekeeping (CUNPK) in India serves as a global peace initiative force that delivers training and capacity development programs for international peace organizations.
What is UN Peacekeeping?
-
UN Peacekeeping acts as an essential framework to achieve global security because it helps uphold peaceful relations between nations. It involves:
-
Political Frameworks: The establishment of political frameworks combined with governance structures receives support through this strategy.
-
Protecting Civilians: Peacekeeping operations must safeguard the civilian inhabitants located in war-torn regions.
-
Disarmament, Demobilization, and Reintegration (DDR): The DDR component supports combatants who left their military roles by helping them become civilians.
-
Election Support: The organization supports democratic procedures through its electoral operations.
-
Human Rights and Rule of Law: Promoting justice, accountability, and governance reforms.
-
India's Contribution to UN Peacekeeping
India started its United Nations peacekeeping operations during the Korean War battle of 1950-1954. The Indian government has sent military personnel alongside medical and logistical participants to many battle zones since the 1950s.
Current Missions with Indian Involvement
|
Mission Name |
Location |
India’s Contribution |
|
UNDOF |
Golan Heights |
Logistics Battalion with 188 personnel |
|
UNIFIL |
Lebanon |
Infantry battalion group with 762 personnel |
|
UNTSO |
Middle East |
Military observers and support staff |
|
UNFICYP |
Cyprus |
Military observers and staff officers |
|
MONUSCO |
Democratic Republic of Congo |
Infantry battalions, medical units |
|
UNMISS |
South Sudan |
Infantry battalion, medical personnel |
|
UNIFSA |
Abyei |
Military observers and staff officers |
|
MINUSCA |
Central African Republic |
Formed Police Units and military observers |
|
MINURSO |
Western Sahara |
Military observers |
The dedication of Indian peacekeeping forces is exceptional because exactly 180 members lost their lives during peace operations.
Women in Peacekeeping
-
Women contribute fundamentally to peacebuilding endeavors and also serve effectively as peace fixers and ingredient participants in conflict resolutions. Through their leadership role India performs the following functions:
-
Indian female troops established the first all-female Formed Police Unit (FPU) in Liberia during 2007 which boosted local women to pursue careers in security services.
-
Major Radhika Sen clinched the UN Military Gender Advocate of the Year award in 2023 for her important contributions.
-
Indian peacekeeping missions currently benefit from the presence of more than 150 female defense personnel who help enhance both security standards and inclusivity throughout the operations.
-
India actively backs the UN goal to reach 15% female military contingent representation along with 25% female police unit participation by 2028.
-
Training and Capacity Building
-
The India-based Centre for United Nations Peacekeeping (CUNPK) in New Delhi maintains an essential function by:
-
The training institution equips more than 12000 peacekeeping troops each year.
-
Through its international programs the establishment runs the United Nations Peacekeeping Course for African Partners (UNPCAP).
-
The plans include organizing the 'Conference on Women Peacekeepers from the Global South’ as a global event in 2025 to promote gender inclusion in peacekeeping operations.
-
Challenges and Future Outlook
-
India has achieved impressive milestones but numerous hurdles continue to affect its peacekeeping efforts.
-
Security risks in volatile regions.
-
Resource constraints in peacekeeping missions.
-
More leaders should come from both genders to achieve higher organizational representation.
-
-
India upholds its commitment to advancing United Nations peacekeeping operations by implementing new technology and conducting diplomatic relations and delivering consistent leadership for educational and capacity development programs.
Conclusion
Units from India have established themselves in UN peacekeeping operations through their determined pursuit of international peace alongside their willingness to forfeit lives for this cause. By providing major troop numbers India maintains a strong impact on global peacekeeping operations through superior military leadership practices and inclusive gender policies and strategic international alliances. India will continue applying principles of dialogue and diplomacy and global cooperation to advance its status as a peace champion in the present global transformation.


 What Were The Reasons That Led To The Arrest Of Ex-Philippine President Rodrigo Duterte?
What Were The Reasons That Led To The Arrest Of Ex-Philippine President Rodrigo Duterte? India-Mauritius Relations: Strengthening Strategic and Cultural Ties
India-Mauritius Relations: Strengthening Strategic and Cultural Ties India’s Growing Economic Footprint in Dubai: A New Era of Bilateral Ties
India’s Growing Economic Footprint in Dubai: A New Era of Bilateral Ties New Delhi to Host 20-Nation Security Meet: Key Agendas and Implications
New Delhi to Host 20-Nation Security Meet: Key Agendas and Implications India- Belgium’s Defence Cooperation in Indo-Pacific region
India- Belgium’s Defence Cooperation in Indo-Pacific region EU and India: Strengthening Ties Amidst Global Shifts
EU and India: Strengthening Ties Amidst Global Shifts Bhutan’s Strategic Role in India’s Regional Diplomacy: Budget 2025-26 Insights
Bhutan’s Strategic Role in India’s Regional Diplomacy: Budget 2025-26 Insights Blue Ghost Lunar Landing: Firefly Aerospace’s Historic Moon Mission
Blue Ghost Lunar Landing: Firefly Aerospace’s Historic Moon Mission India-EU Strategic Partnership: Advancing Trade, Security, and Economic Cooperation
India-EU Strategic Partnership: Advancing Trade, Security, and Economic Cooperation






