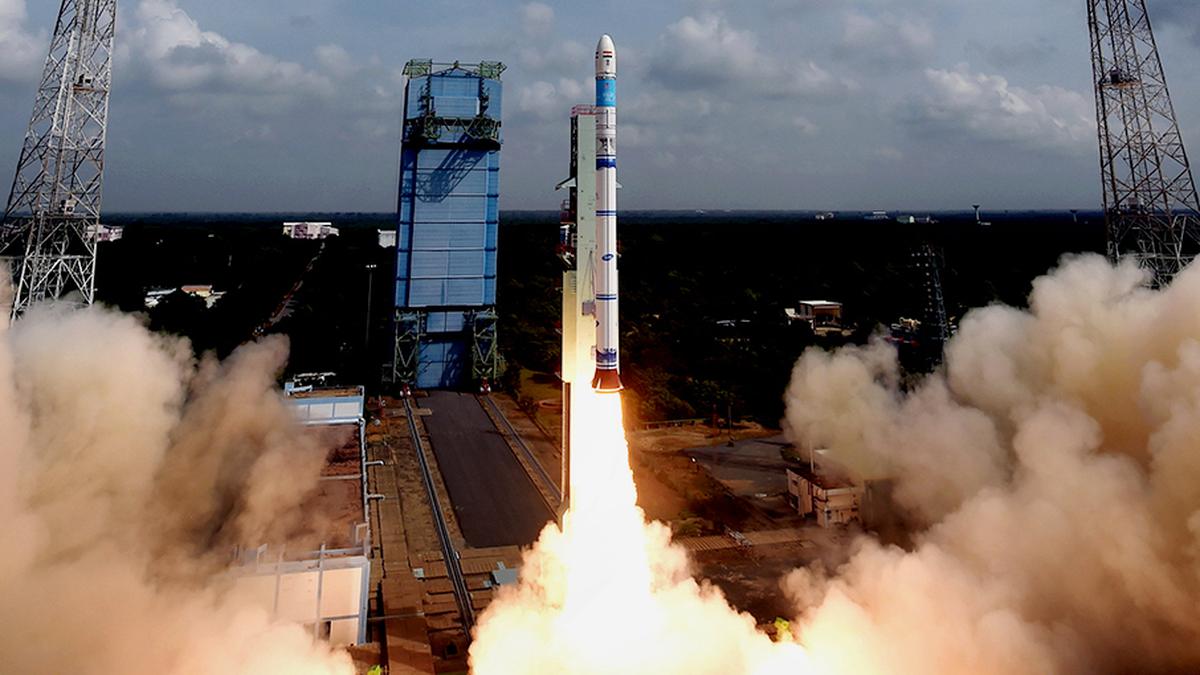

ISRO is poised to mark a significant milestone in January 2025 with its 100th mission, the launch of the NVS-02 satellite aboard the GSLV Mark II. This advanced satellite will serve as the ninth addition to the NavIC navigation system, enhancing positioning accuracy and boosting navigation capabilities. Equipped with a Rubidium atomic clock and advanced payloads, the NVS-02 satellite promises to provide precise location tracking and improved interoperability with global systems. This mission highlights India’s progress in autonomous navigation technology and its commitment to strengthening its space infrastructure.
ISRO plans to carry out its 100th mission by launching the NVS-02 satellite on the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) in January 2025. India's space development program is achieving important progress after this milestone launch.
About the NVS-02 Satellite:
-
Technology has reached a milestone as NVS-02 marks the ninth satellite entry in NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation) while firmly serving as the second delivery in its 2nd-generation navigation satellite progress.
-
Launch vehicle: GSLV Mark II.
Payloads of NVS-02:
-
Navigational Payload:
-
Users on Earth receive transmitted signals through the L1, L5, and S-band frequencies.
-
Precise time measurements become possible thanks to the onboard Rubidium atomic clock system which delivers positioning accuracy to within less than 10 nanoseconds.
-
-
Ranging Payload:
-
The system supports user navigation through its transponder designed to send timestamped tracking signals that deliver precise position speed determination and time accuracy even in harsh weather environments.
-
Significance of 2nd Generation Satellites:
-
Enhanced interoperability with other global satellite systems due to the additional L1 frequency.
-
The extended mission life of 2nd-generation satellites reaches over 12 years giving longer mission life whereas the first generation operates for only 10 years
-
Improved encryption for secure communications.
What is NavIC?
-
NavIC stands as India's independent satellite navigation system under the title Navigation with Indian Constellation.
-
NavIC consists of seven satellites positioned to provide positioning navigation timing services to India and its neighboring regions.
Key Objectives of NavIC:
-
NavIC serves three primary functions including defense operations along with emergency service systems and strategic missions.
-
Precision agriculture, geodetic surveying, and timing services for financial institutions.
Global Comparison:
-
Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS): GPS (USA), GLONASS (Russia), BeiDou (China), Galileo (EU), and Japan’s QZSS.
Why NavIC?
-
India's autonomous positioning system enhances national security alongside military operations by operating without needing external worldwide satellite systems.
Conclusion
NVS-02 satellite launch represents a vital achievement for ISRO and the Indian space program which both improves NavIC system capabilities, provides better navigation services and boosts national defense capabilities.


 ISRO to Send Tardigrades on Axiom-4 Mission: A Step Towards Advancing Space Research
ISRO to Send Tardigrades on Axiom-4 Mission: A Step Towards Advancing Space Research TERI's Nano Sulphur Breakthrough in Mustard Cultivation
TERI's Nano Sulphur Breakthrough in Mustard Cultivation ISRO's Successful Second Docking of Satellites – A Milestone in Space Technology
ISRO's Successful Second Docking of Satellites – A Milestone in Space Technology Potential Biosignatures Discovered on Exoplanet K2-18b by JWST
Potential Biosignatures Discovered on Exoplanet K2-18b by JWST India Launches First Native Seed Germination Database for Ecological Restoration
India Launches First Native Seed Germination Database for Ecological Restoration India’s Evolving Approach to Artificial Intelligence Governance and Regulation
India’s Evolving Approach to Artificial Intelligence Governance and Regulation Golden Jubilee of Aryabhata 2025: Celebrating India’s First Satellite and ISRO’s Historic Milestone
Golden Jubilee of Aryabhata 2025: Celebrating India’s First Satellite and ISRO’s Historic Milestone ESA's Biomass Mission 2025: Tracking Global Forest Carbon Storage via Satellite
ESA's Biomass Mission 2025: Tracking Global Forest Carbon Storage via Satellite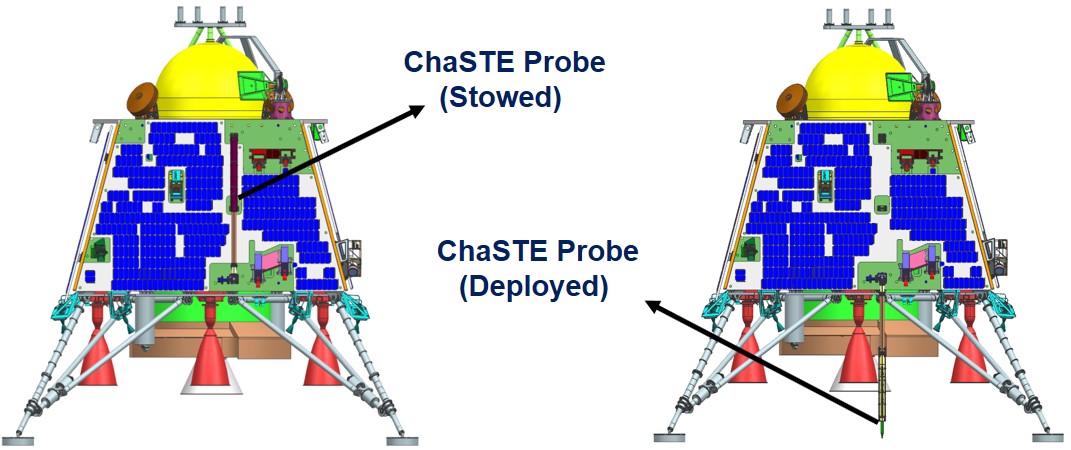 ChaSTE: First In-Situ Measurement of Surface Temperature
ChaSTE: First In-Situ Measurement of Surface Temperature Digital Child Abuse and the Dangers of AI-Based Exploitation
Digital Child Abuse and the Dangers of AI-Based Exploitation






