
Medical education presently experiences an odd state where doctors are seen as scarce but patient care remains difficult to access. Because Indian students find both extremely competitive conditions and high fees for private education too prohibitive they select global medical institutions in Russia, Ukraine, and China where more than 200,000 currently study. New medical graduates encounter two major obstacles which include NExT tests in addition to internship requirements. Indian institutions continue to establish educational campuses overseas to address rising student enrollment demands.
The number of medical immigrants continues to increase worldwide since European and American students opt for other options. The Indian government intends to establish 75,000 new medical education seats throughout five years. Government policies need to make medical education accessible across all levels while maintaining quality standards through strategically expanding domestic programs and international partnerships. This approach will create a standardized medical education system in India.
Introduction
-
Doctor shortages exist amid restricted opportunities for medical seat admission in medical educational programs across the globe.
-
Indian students leave for medical degree programs both due to tuition fee expenses and competitive university admission barriers.
-
The worldwide issue Government bodies encounter involves maintaining a balance between medical education costs and enrollment levels and educational standards.
Challenges in Indian Medical Education
-
Shortage of Seats
-
A total of 2.3 million Indian students attempt to enter available medical training positions at 700+ medical institutions.
-
The competition rate for admission is extremely high since only one student out of twenty-two successfully gains entrance.
-
-
High Cost of Private Medical Education
-
Government medical colleges cannot meet the demand due to restricted enrollment yet private medical education costs a large sum of money.
-
The reduced cost of education in foreign medical universities leads many students to enroll there.
-
Medical Brain Drain and Its Impact on India
-
The number of Indian students studying medicine outside their nation surpasses 200,000.
-
Students tend to study medicine in the countries which include Russia together with Ukraine as well as Kazakhstan with China and Nepal.
-
International students faced increased risks because Russia invaded Ukraine which revealed the weaknesses associated with studying abroad.
-
Newly returning doctors encounter two important hurdles which include NExT tests and required internship service.
India’s Role in Global Medical Education
-
Indian institutions have started creating medical college campuses overseas.
-
Two institutions founded by Indian organizations operate as Manipal College of Medical Sciences (Nepal) and the American University of Antigua (Caribbean).
-
The establishment of new medical educational facilities provides solutions for worldwide medical education expansion.
Global Trends in Medical Migration
-
Medical migration exceeds numbers in both South Asia and Africa.
-
European students from France, Germany, Norway, and the Netherlands move to Hungary, Poland, and Romania for medical studies.
-
American medical students enroll in Ireland the Caribbean and Hungary along with the United Kingdom because they cannot secure admission to their desired institutions.
Commercialization of Medical Education
-
The fundamental priority of private medical institutions to generate profits leads to a deterioration of educational standards.
-
Educational facilities from unidentified institutions do not comply with training quality standards.
-
Governments face substantial challenges in properly managing medical training programs that operate across national borders.
Government Initiatives and Policy Reforms
Expansion of Medical Seats
-
The addition of 1.1 lakh medical seats throughout the last decade led to a 130% increase in total medical seats.
-
The institution aims to establish 10,000 additional seats throughout its expansion project which will grow medical seat availability to 75,000 by 2026.
Regulation of Foreign Medical Education
-
The NExT exam verifies that medical graduates returning to India have reached proficiency levels established by Indian medical standards.
-
Indian medical facilities must establish binding agreements with foreign educational organizations to maintain standards of excellence.
Strengthening Domestic Medical Infrastructure
-
The domestic medical infrastructure needs expansion by building more medical institutions together with hospital training facilities and public health investment initiatives.
Conclusion
-
The solution to India's medical practitioner shortage requires an increase in medical educational capacity throughout the nation.
-
All policy changes need to address quality standards with cost control alongside service availability for the medical field.
-
A properly controlled medical education system across the globe needs to uphold consistent standards.



 Param Rudra Supercomputer Launched at IIT-Patna
Param Rudra Supercomputer Launched at IIT-Patna Rashtra Prerna Sthal Inaugurated to Honour Atal Bihari Vajpayee
Rashtra Prerna Sthal Inaugurated to Honour Atal Bihari Vajpayee Homebound Nominated for Oscars 2026: Kiara Advani, Zoya Akhtar Call It ‘EPIC’
Homebound Nominated for Oscars 2026: Kiara Advani, Zoya Akhtar Call It ‘EPIC’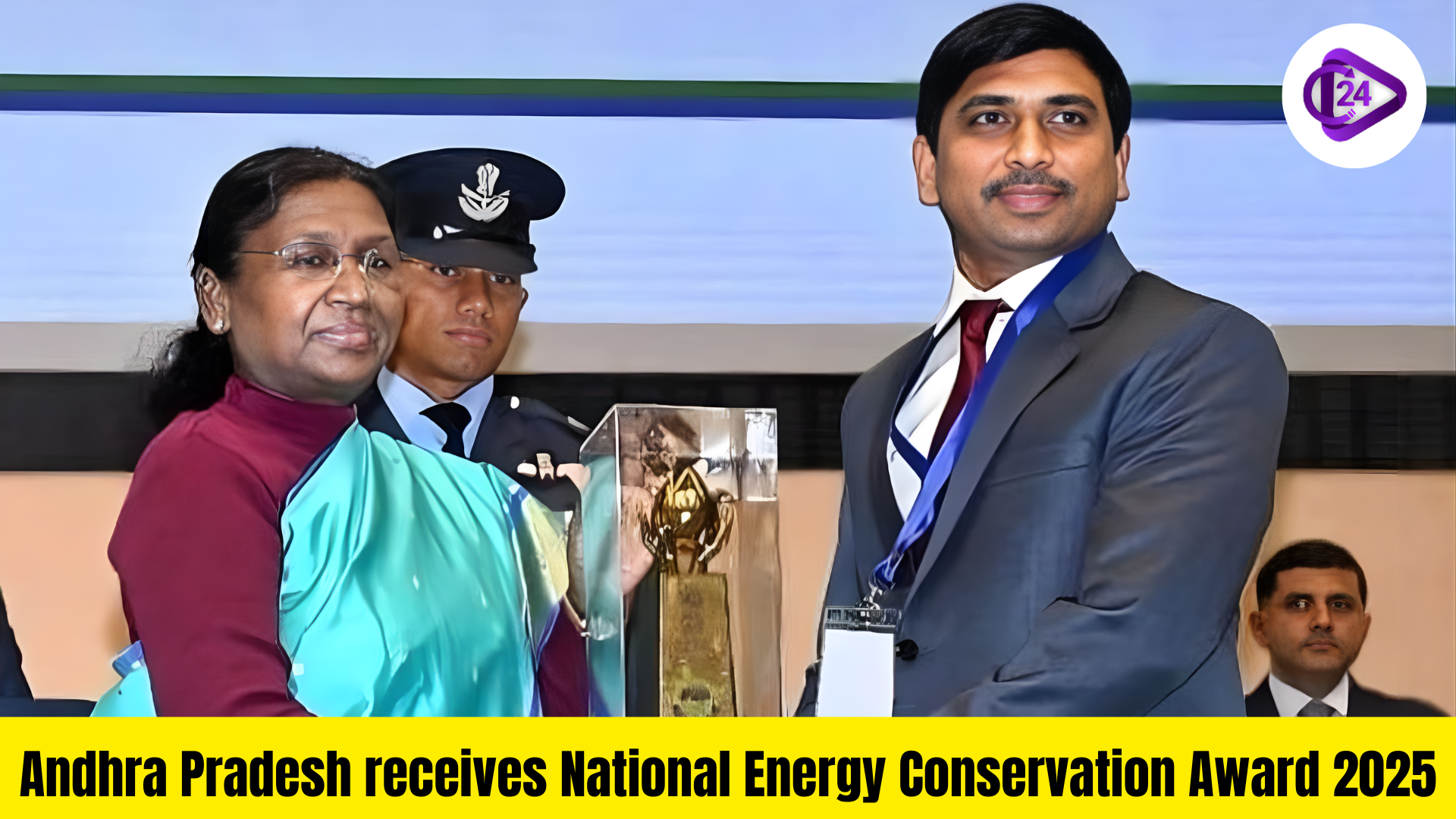 Andhra Pradesh Receives National Energy Conservation Award from President Murmu
Andhra Pradesh Receives National Energy Conservation Award from President Murmu Centre Plans to Rename MGNREGS to ‘Pujya Bapu Gramin Rozgar Yojana’
Centre Plans to Rename MGNREGS to ‘Pujya Bapu Gramin Rozgar Yojana’ Bihar to Establish India’s First Power Museum in Patna
Bihar to Establish India’s First Power Museum in Patna UPI is the World’s Largest Fast-Payment System: IMF Report
UPI is the World’s Largest Fast-Payment System: IMF Report Microsoft Commits $17.5 Billion to Accelerate India’s AI Future
Microsoft Commits $17.5 Billion to Accelerate India’s AI Future Government, Opposition spar in Lok Sabha over Vande Mataram
Government, Opposition spar in Lok Sabha over Vande Mataram Mahad Satyagraha Shaped The Indian Constitution
Mahad Satyagraha Shaped The Indian Constitution






