
India has come out decisively during the GA of Global Plastic Treaty in Busan opposing any proposed mandatory prescriptions of specific forms of plastic substitution without reference to the country’s priorities. In this regard, India pointed to the basic need to respond to the growing problem of global plastics pollution, while taking cognizance of the fact that they should do so in a fair, sustainable manner, which takes into account the development status of all countries and their industrial capabilities. Continuing to fight for sustainable innovation, the leadership of India stressed that they are seeking for real solutions with partly removing obstructions to domestic industries and economic growth.
Highlights of Equitable Distribution System in India
India raised concerns over the fact that developed countries continues to contribute to plastic waste emissions more than developing countries and urged the parties to put much pressure unto these developed nations. Superior technological apparatus and assets available in the developed countries put them in a better place to apply and encourage sustainable substitutes. On the other hand developed countries have relatively less problems such as financially resources and availability of resources to recycle and dispose off wastes. India categorically affirmed that policies under the treaty cannot challenge these realities nor is it must subscribe to developmental objectives of nations such like India.
College Essay: The Interconnectedness of ENvironmentalism and Economics
Thus reaffirming the commitment to sustainable development India cited the necessity of non-regression of domestic industrial growth by international agreements at WTO. As in many other nations, cheap and easily available plastic material is still commonly used by a number of small and medium entrepreneurial ventures in India. The capital intensive sectors could experience a blow which ultimately lead to loss of jobs as firms transform to the new materials. India also highlighted the importance of the integrated approach that would help to avoid damages done to the environment as well as any sharper fluctuations on the markets.
Treaty negotiations Summarised Points
-
Reduction of Plastic Production: The treaty is meant to establish frameworks for reductions of plastics manufacture in the world.
-
Promotion of Alternatives: One of the positive effects is that transforms research and development of sustainable materials as a replacement to typical plastics.
-
Waste Management: Current topics range from better ways of collecting and promoting the recycling and safe disposal of plastic waste across the globe.
Indian initiative in the actual bargaining also exemplifies diplomacy in how it tried to forward international environmental objectives and Indian interests at the same time. For SSC and UPSC aspirants, this breaking news covers important topics under international news and Environment & Sustainable Development.



 RBI Retains SBI, HDFC Bank, and ICICI Bank as Domestic Systemically Important Banks
RBI Retains SBI, HDFC Bank, and ICICI Bank as Domestic Systemically Important Banks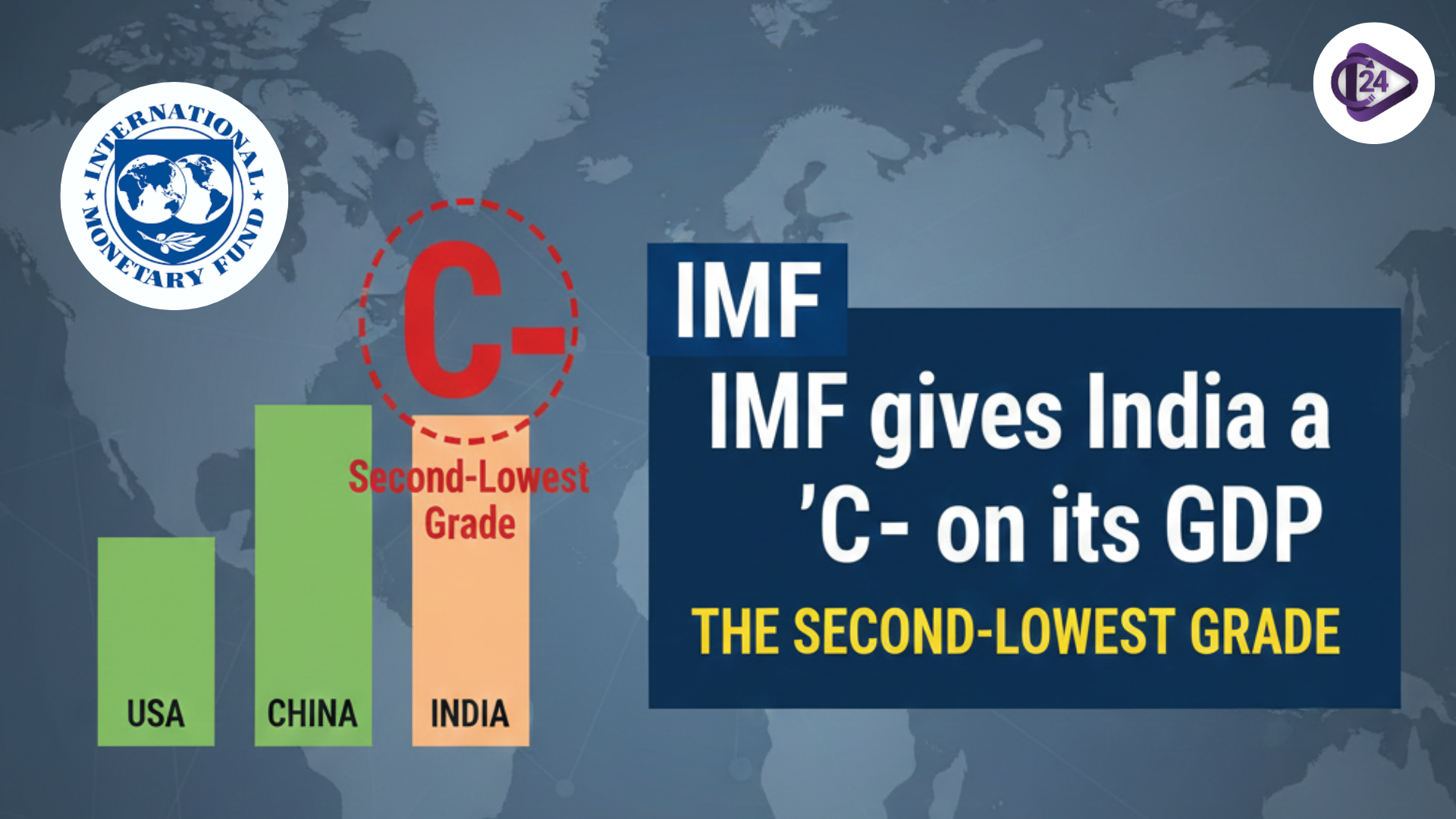 IMF gives India a ‘C’ on its GDP and other national accounts data, the second-lowest grade
IMF gives India a ‘C’ on its GDP and other national accounts data, the second-lowest grade India Witnesses Rapid Surge in Ultra-Processed Food Consumption
India Witnesses Rapid Surge in Ultra-Processed Food Consumption HDFC Bank Secures the Top Rank in India’s 2025 Brand Value Index
HDFC Bank Secures the Top Rank in India’s 2025 Brand Value Index ASSOCHAM New President Nirmal Minda to Drive Industrial Innovation and Sustainability in India
ASSOCHAM New President Nirmal Minda to Drive Industrial Innovation and Sustainability in India 8th Pay Commission 2025: Latest News, Salary Hike & DA Update
8th Pay Commission 2025: Latest News, Salary Hike & DA Update Sonali Sen Gupta Takes Charge as RBI Executive Director
Sonali Sen Gupta Takes Charge as RBI Executive Director Shram Shakti Niti 2025: India’s Future-Ready Labour Policy for Employment Growth
Shram Shakti Niti 2025: India’s Future-Ready Labour Policy for Employment Growth Secure UPI Transactions: RBI and NPCI Introduce Biometric Authentication
Secure UPI Transactions: RBI and NPCI Introduce Biometric Authentication Shirish Chandra Murmu Appointed as RBI Deputy Governor
Shirish Chandra Murmu Appointed as RBI Deputy Governor






