
3rd December 2024 is celebrated as International Day of Persons with Disabilities 2024 (IDPD) every year since 1992, as declared by the United Nations(UN). It is an initiative to make an inclusive society where people with disability are more empowered and are given equal opportunities and rights. This is celebrated every year globally to make people more aware of the rights of people with a disability and to highlight their achievements.
President of India to confer National Awards for Empowering Persons with Disabilities to 33 exemplary individuals and institutions on the occasion of International Day of Persons with Disabilities 2024 in New Delhi tomorrow
On the occasion, Union Minister for Social Justice and Empowerment, Dr Virendra Kumar, will unveil 16 transformative initiativesto enrich the lives of Persons with Disabilities. Some of them are the Kadam Knee Joint in collaboration with IIT Madras &SBMT Bengaluru, the introduction of high-powered spectacles, the inauguration of the “Divyasha” e-coffee table book, Sugamya Bharat Yatra MoU, Braille Book Portal,etc.
Background
- 1992: It was first celebrated in the year 1992 as the UN declared 3rd December as International Day of Persons with Disabilities 2024 (IDPD) to give persons with disabilities their social, political and economic rights and to highlight the challenges faced them and to provide a solution to it.
- 2006: An international treaty namedthe Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD) was adopted in 2006, which promoted equal rights of persons with disabilities (PWD) globally. This contributed to creatingthe Sustainable Development Goals(SDG) 2030 framework.
Theme for 2024: “Amplifying the leadership of persons with disabilities for an inclusive and sustainable future.”
What is disability?
It is a condition in which a person cannot function fully as compared to another person who can function with his full potential. It can be physical, mental, or both. The disability works as a barrier in an individual's life as it restricts one’s potential to function compared to others fully.
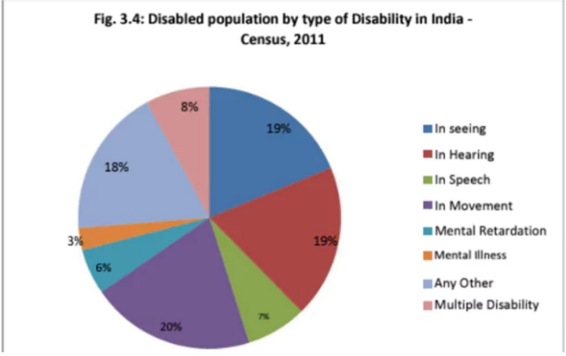
Types of disabilities
The most common types of disabilities in India, according to the Census data, include:
- Locomotor disability: 30.5%
- Visual impairment: 19.3%
- Hearing impairment: 18.9%
- Speech impairment: 5.6%
- Mental illness/disability: 5.6%
- Multiple disabilities: 5.5%
As per the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016 (RPwD Act), the Government of Indiarecognises21 types of disabilities to ensure empowerment, equal rights &opportunities& inclusive society. Here is a list of types of disabilities as per the government of India:·
Data Point
Global Statistics:
- 1 billion people (15% of the global population) live with some form of disability.
- 46% of people aged 60 and above experience some form of disability.
- 80% of PwDs live in developing countries, facing more significant service access challenges.
Indian Statistics:
- 2.68 crore (26.8 million) PwDs in India (2.21% of the population per the 2011 Census).
- Most common disabilities: Locomotor disability (30.5%), visual impairment (19.3%), and hearing impairment (18.9%).
- Higher prevalence in rural areas compared to urban areas.
- Government initiatives like the RPwD Act, 2016, aim to improve accessibility, education, and employment for PwDs.
Legal rights of PWD
Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016: This law recognises 21 types of disabilities, including locomotor disability, visual/hearing impairments, and intellectual disability.
- 40% of people are categorised under people with benchmark disabilities
- 5% reservation to children with disabilities with age between 6-28 years for higher education
- 4% reservation for people with disabilities in government jobs
- Public buildings must be accessible for PWD
- National & state funds are created for providing financial assistance to PWD
Constitutional Provisions
- Article 14: Guarantees equality before the law.
- Article 21: Ensures the right to live with dignity.
- Article 41: Directs the state to provide public assistance to people with disabilities.
Legal Protections
- The Mental Healthcare Act, 2017: Safeguards the rights of individuals with mental illnesses.
- The Rehabilitation Council of India Act, 1992: Regulates training and policies for rehabilitation professionals
Govt initiatives for PWD
|
NIRAMAYA: |
Health insurance for autism, cerebral palsy, mental retardation, and other disabilities at very low prices. |
|
GYAN PRABHA: |
Educational support for those with autism, cerebral palsy, mental retardation, and multiple disabilities. |
|
Indira Gandhi National Disability Pension Scheme: |
Rs 500-1000 (varies state to state) of monthly pension for disabled people aged 18 or older with a disability of 80% or more, belonging to the poverty line |
|
ADIP Scheme |
This schemes provides aid to PWD. |
|
Marriage Incentive Award |
₹30000 allowance for eligible individuals having disabilties |
|
DivyangjanSwavalamban Yojana: |
Concessional loans for economic empowerment. |
|
Divya Kala Mela |
A national-level fair where divyang artisans show their talent & skills in arts and crafts etc. |
|
PM-DAKSH Yojana |
A platform for skill training of divyangs where they can get livelihood and can be economically empowered. |
Chat With Us

 India Secures re-election UN Peacebuilding Commission 2025-2026
India Secures re-election UN Peacebuilding Commission 2025-2026 High Seas Treaty UNCLOS Milestone Marine Conservation
High Seas Treaty UNCLOS Milestone Marine Conservation India Signs Riyadh Design Law Treaty IPR
India Signs Riyadh Design Law Treaty IPR Global Action Against Plastic Pollution Treaty 2025
Global Action Against Plastic Pollution Treaty 2025 India At COP29 2024 Climate Action Global Sustainability
India At COP29 2024 Climate Action Global Sustainability Armenia Joins International Solar Alliance as 104th Member
Armenia Joins International Solar Alliance as 104th Member India Caricom Summit Strengthening Ties Global Cooperation
India Caricom Summit Strengthening Ties Global Cooperation Climate Finance NCQG Global Inequities and Funding Solutions
Climate Finance NCQG Global Inequities and Funding Solutions Adani Group Legal Issues Bribery Fraud Global Impact
Adani Group Legal Issues Bribery Fraud Global Impact






